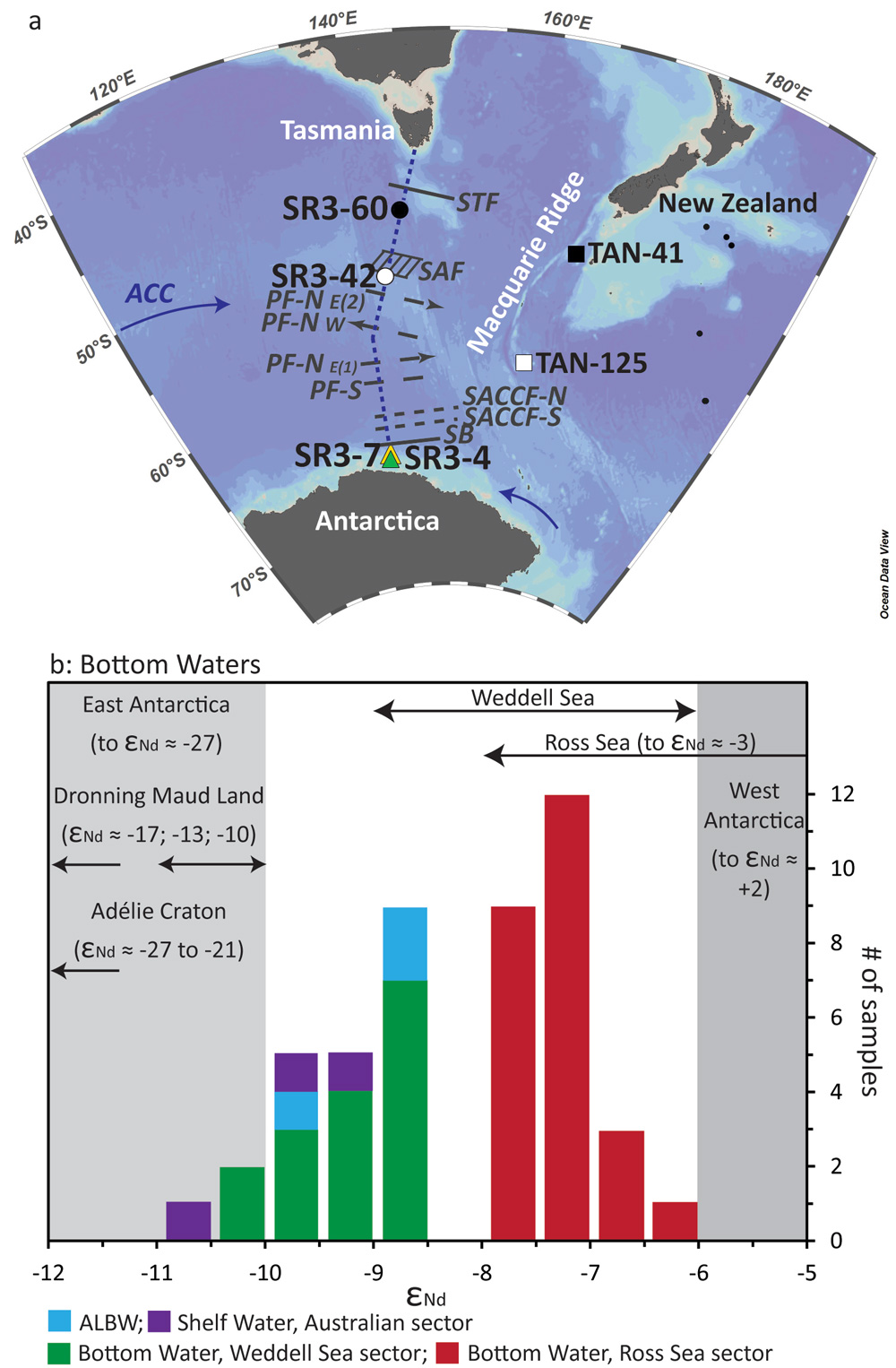
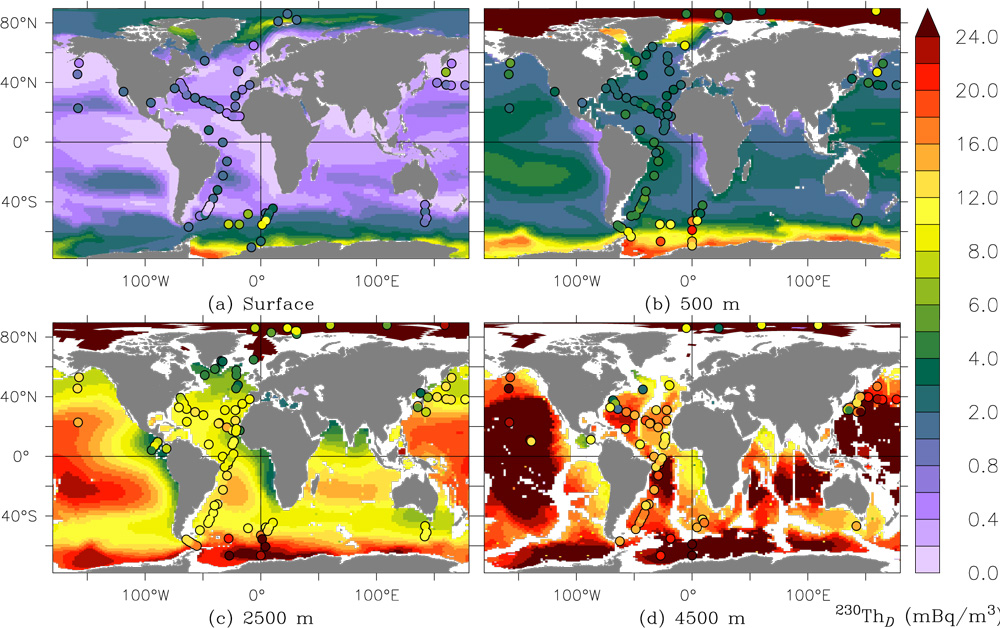
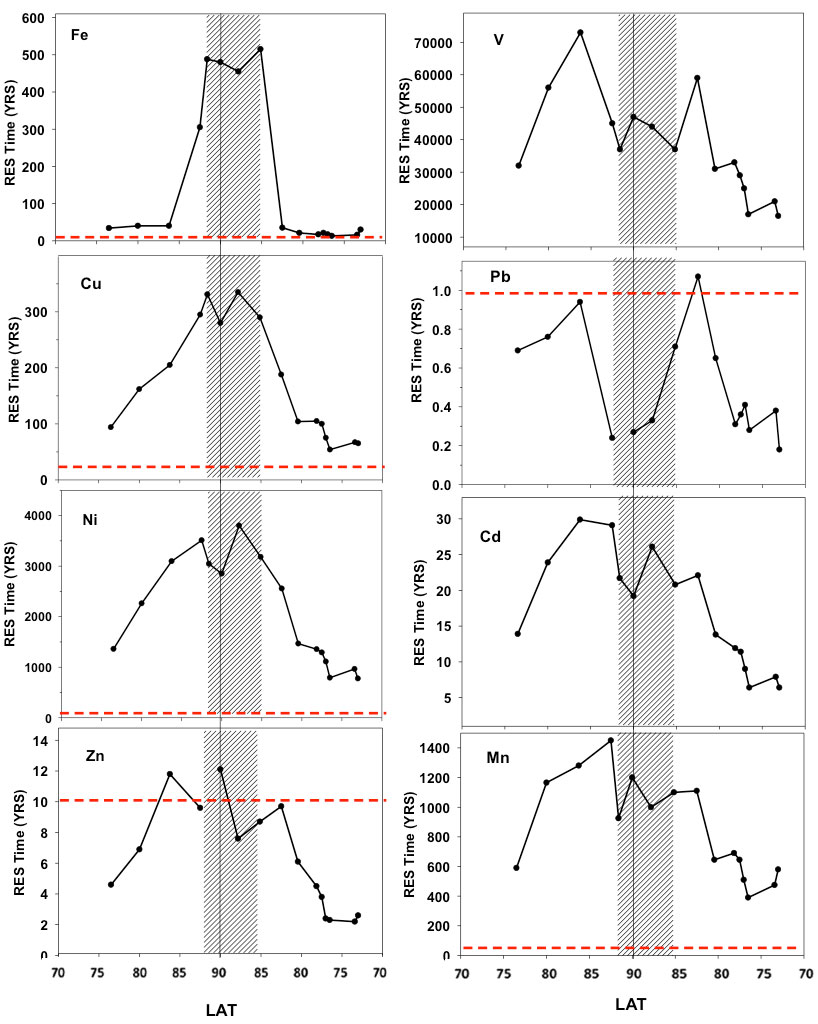
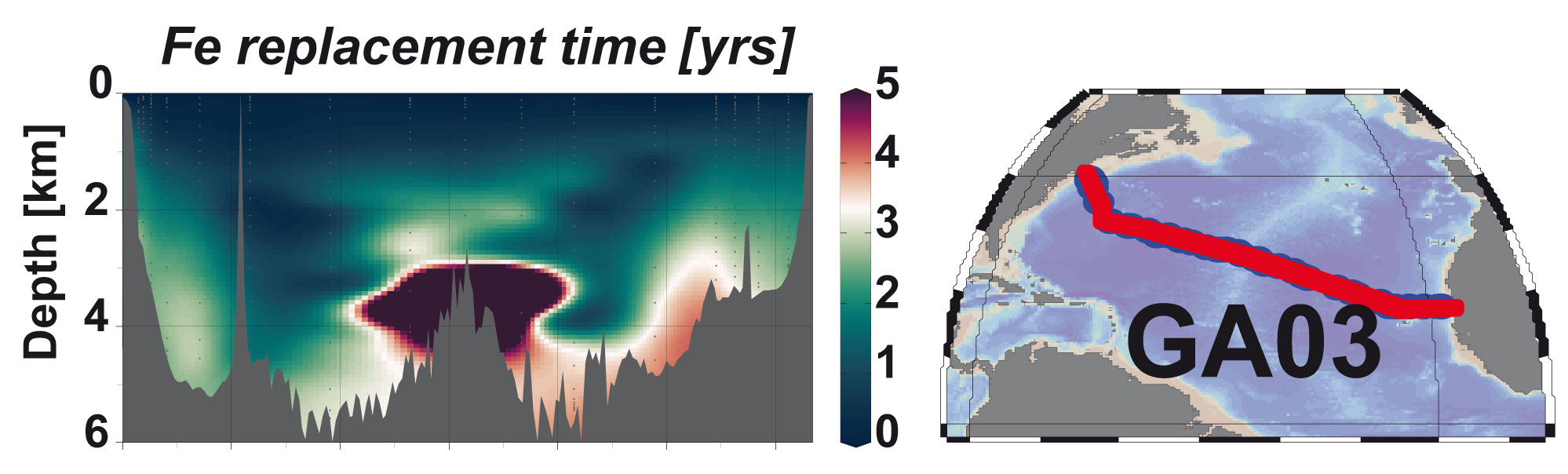
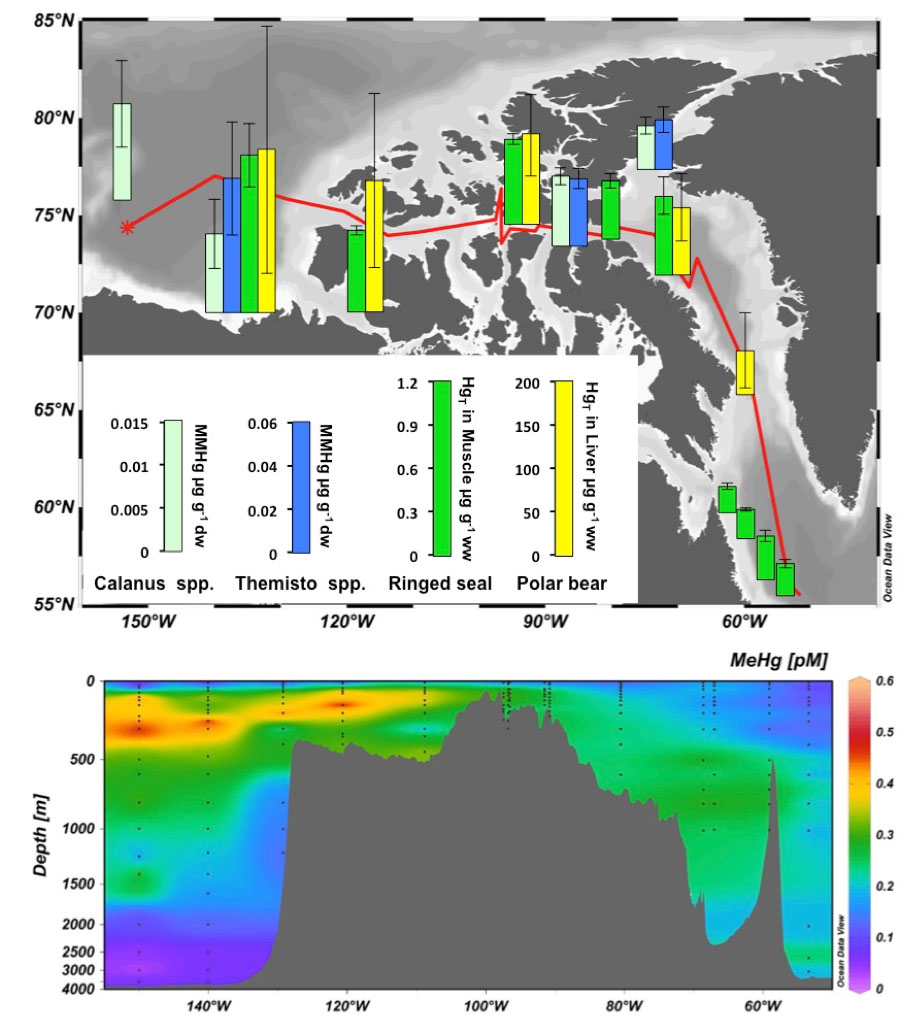
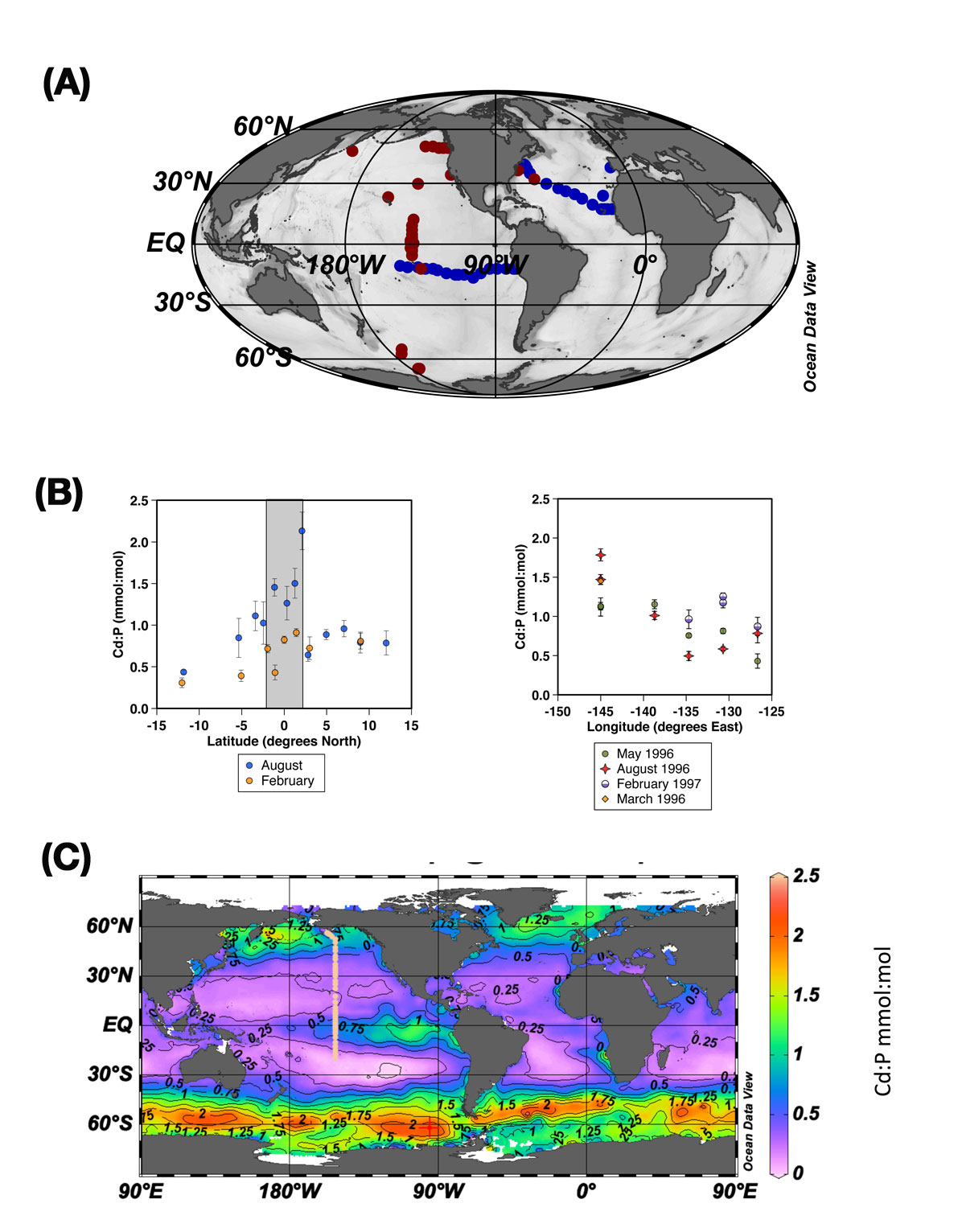
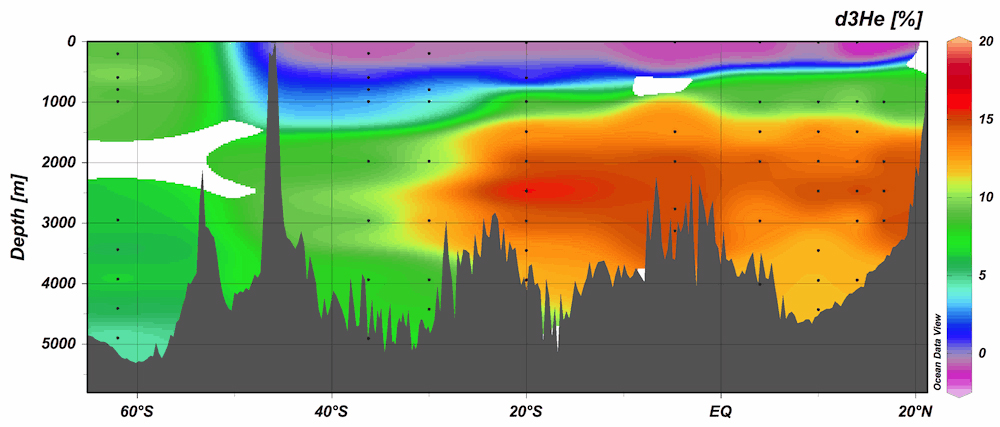
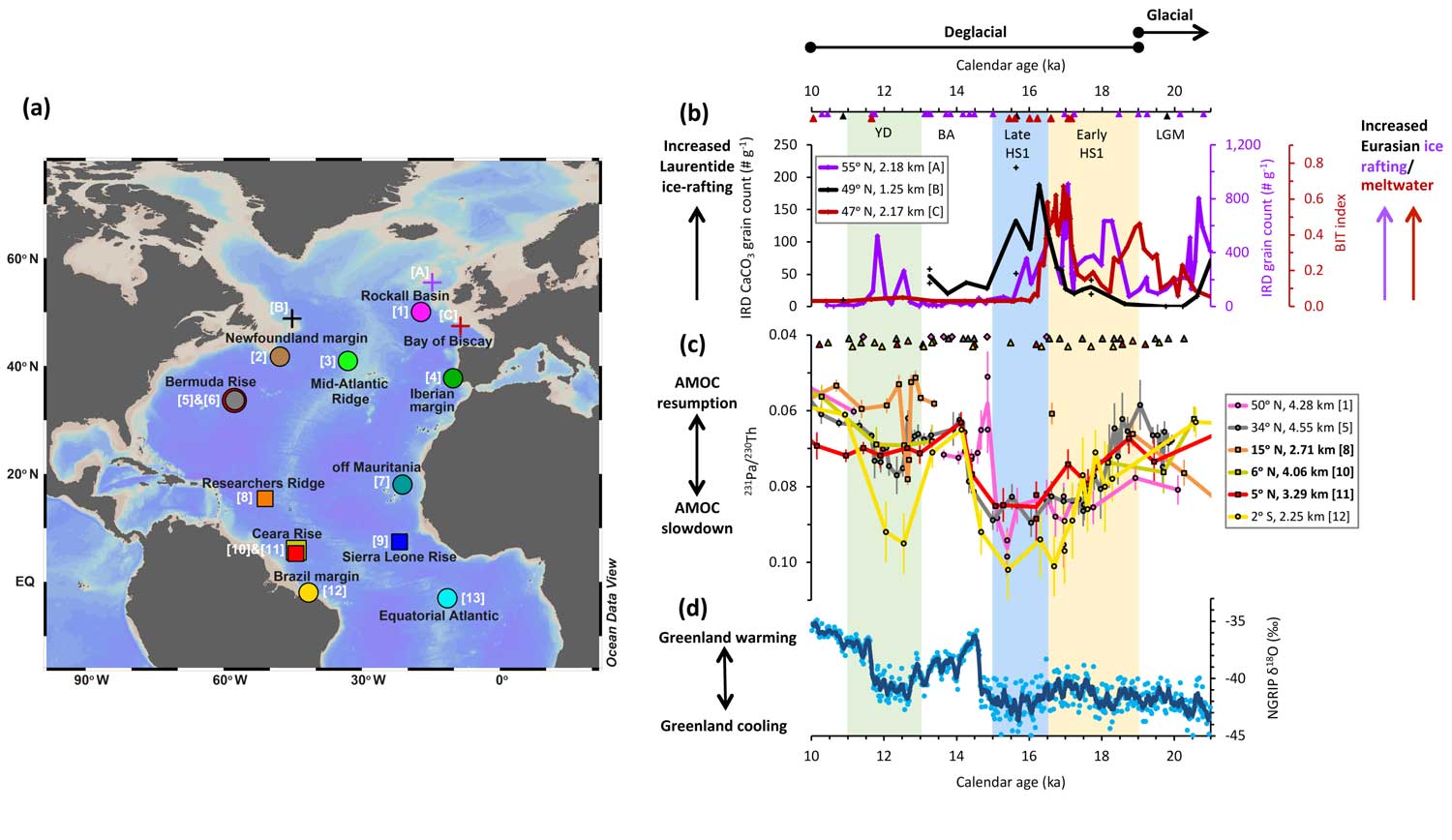
Important spatial variation of the Particulate Organic Carbon export along the GEOVIDE section in the North Atlantic Ocean
Based on the thorium-234 (234Th) isotopes and the Particulate Organic Carbon/Thorium (POC/Th) ratios measured in small and large particles collected at 11 stations along the GEOVIDE section (GA01) using in […]