Important spatial variation of the Particulate Organic Carbon export along the GEOVIDE section in the North Atlantic Ocean
Based on the thorium-234 (234Th) isotopes and the Particulate Organic Carbon/Thorium (POC/Th) ratios measured in small and large particles collected at 11 stations along the GEOVIDE section (GA01) using in situ pumps, exported POC flux relative the surface primary production were determined by Lemaitre and colleagues (2018, see reference below). While a factor of 9 characterizes the spatial variability of the exported flux, comparison with results obtained from other studies in the North Atlantic range from similar to up to 27 times larger values, with rapid changes over a 1-month duration, underlining the large temporal variability of the POC export fluxes in this area. The authors demonstrate significant links between this export, the stage of the bloom and the phytoplankton communities: (1) minimal fluxes when sampling occurred close to bloom peak or where picophytoplankton dominated the community, (2) high POC export fluxes in post-bloom periods and where micro- and nanophytoplankton dominated and (3) the export efficiency is mostly below 14%, in agreement with the global value of this parameter and the highest transfer efficiencies (70-80%) are found at stations where coccolithophorids dominated, thereby confirming their ballasting properties.
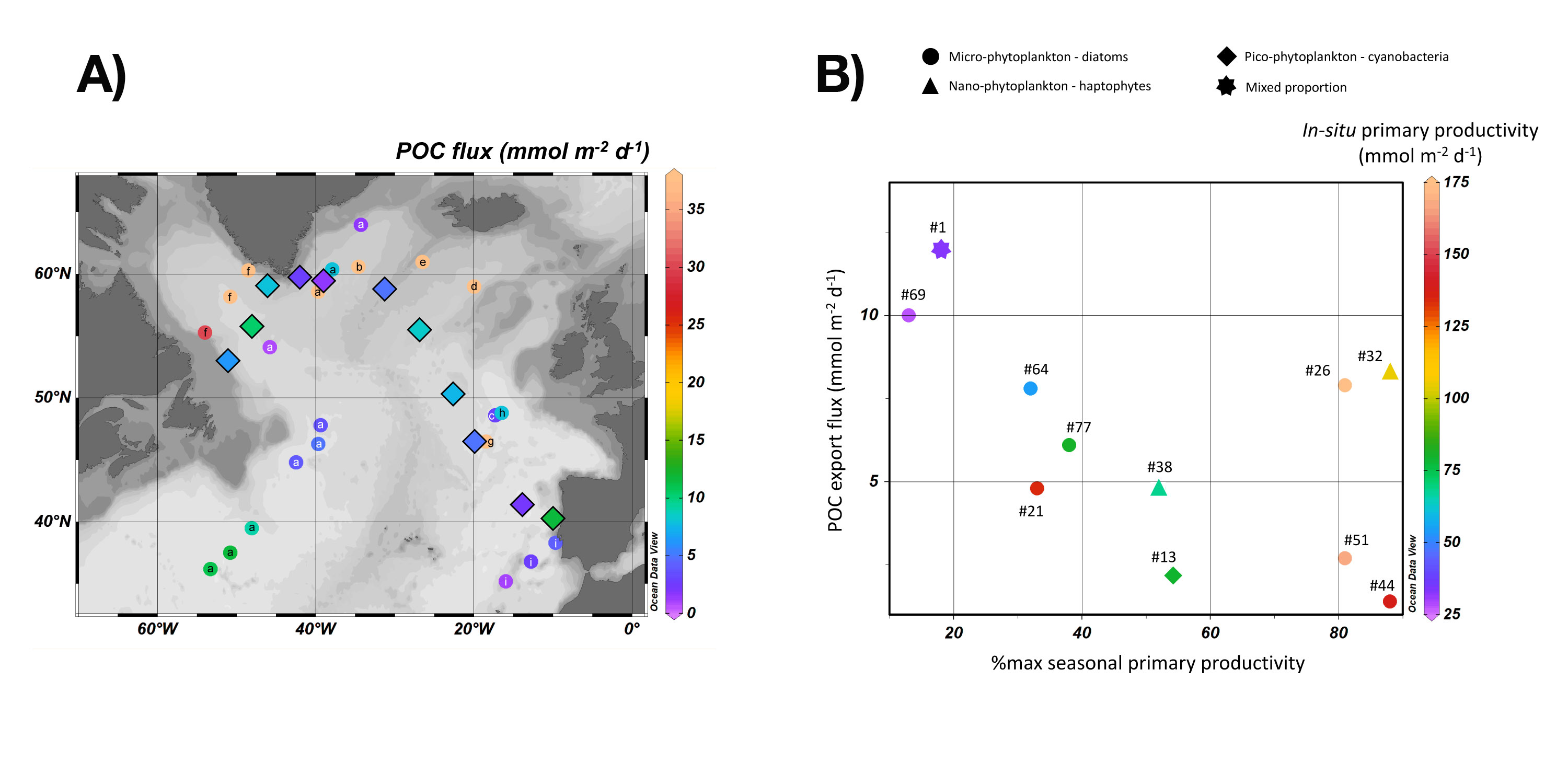 Figures: (A) The map figure highlights the strong spatial variability of the POC export fluxes within the North Atlantic, ranging from 0.7 to 52 mmol C m-2 d-1. Export fluxes deduced during the GEOVIDE cruise (this study, diamond symbols with black borders on the map) either compare well or are in the lower range of values published in the literature. (B) The scatter figure shows the links between POC export fluxes, the stage of the bloom (illustrated by the %max. seasonal primary productivity: a value of 100% corresponds to a sampling time at the bloom peak) and the phytoplankton communities. The bloom intensity at sampling time is also indicated with the colors, indicating in-situ primary productivities. Click here to view the image larger.
Figures: (A) The map figure highlights the strong spatial variability of the POC export fluxes within the North Atlantic, ranging from 0.7 to 52 mmol C m-2 d-1. Export fluxes deduced during the GEOVIDE cruise (this study, diamond symbols with black borders on the map) either compare well or are in the lower range of values published in the literature. (B) The scatter figure shows the links between POC export fluxes, the stage of the bloom (illustrated by the %max. seasonal primary productivity: a value of 100% corresponds to a sampling time at the bloom peak) and the phytoplankton communities. The bloom intensity at sampling time is also indicated with the colors, indicating in-situ primary productivities. Click here to view the image larger.
Reference:
Lemaitre, N., Planchon, F., Planquette, H., Dehairs, F., Fonseca-Batista, D., Roukaerts, A., Deman, F., Tang, Y., Mariez, C., Sarthou, G. (2018). High variability of particulate organic carbon export along the North Atlantic GEOTRACES section GA01 as deduced from 234Th fluxes. Biogeosciences, 15(21), 6417–6437. DOI: http://doi.org/10.5194/bg-15-6417-2018
