Helium-3 plumes in the deep Indian Ocean confirm hydrothermal activity
Thanks to samples collected as part of the Japanese GEOTRACES cruise in 2009 – 2010, along section GI04, Takahata and co-workers (2018, see reference below) identified a maximum helium-3 ratios value (δ3He >14%) at mid-depth (2000 – 3000 m) in the northern part (north of 30°S) of the central Indian Ocean, whereas lower ratio was found in the southern part at the same depth. These values identify an hydrothermal helium-3 plume originating from the Central Indian Ridge around 20°S flowing eastward from the ridge as previously reported in WOCE cruises. Another hydrothermal source of helium-3 is observed in the Gulf of Aden, also helping to constrain the deep circulation off the North East African coast.
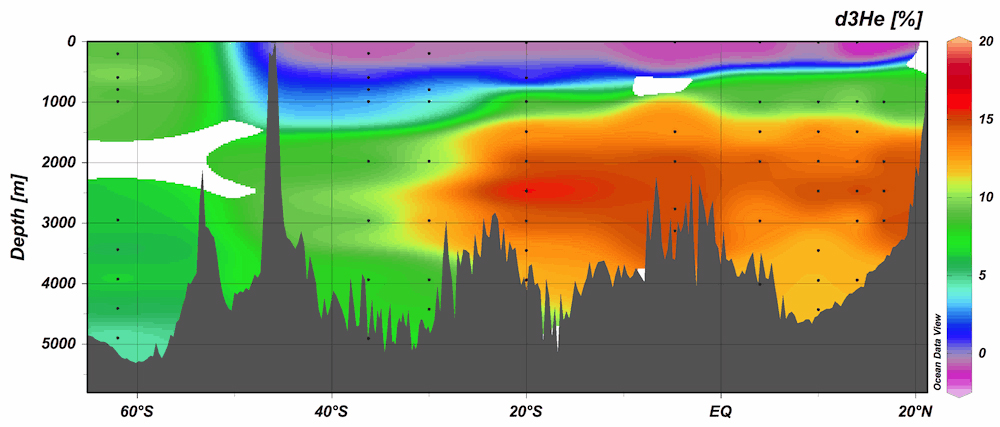
Figure: Vertical distribution of excess helium-3 (3He) along 70˚E of the central Indian Ocean. Two hydrothermal plumes are identified at mid-depth; one is from the Central Indian Ridge and the other from Gulf of Aden. Click here to view it larger.
Reference:
Takahata, N., Shirai, K., Ohmori, K., Obata, H., Gamo, T., & Sano, Y. (2018). Distribution of helium-3 plumes and deep-sea circulation in the central Indian Ocean. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 29(3), 331–340. http://doi.org/10.3319/TAO.2017.10.21.02
