Ever wonder how long your favourite element remains in the ocean before it’s gone again?
This timeframe, sometimes called a residence time, ranges from decades for the most reactive trace elements to millions of years for the most unreactive elements such as the major components of sea salt. The residence time is often difficult to constrain and involves estimating how much of an element is presently in the ocean (i.e., the inventory) as well as the magnitude of the total supply rate or removal rate of the element. In the study published by Hayes and co-authors in Global Biogeochemical Cycles (2018, see reference below), a replacement time (or residence time with respect to supply) can be quantified using large synthesized GEOTRACES datasets from the North Atlantic which can precisely define the inventory of trace elements as well as their supply rate using radioactive tracers. In particular, their method suggests an ocean replacement for iron that is only 6 years, meaning this micronutrient element may be cycling much more quickly than previous estimates have suggested and will provide a target for ocean models to understand how this element is removed from the ocean in terms of biological uptake or abiotic scavenging.
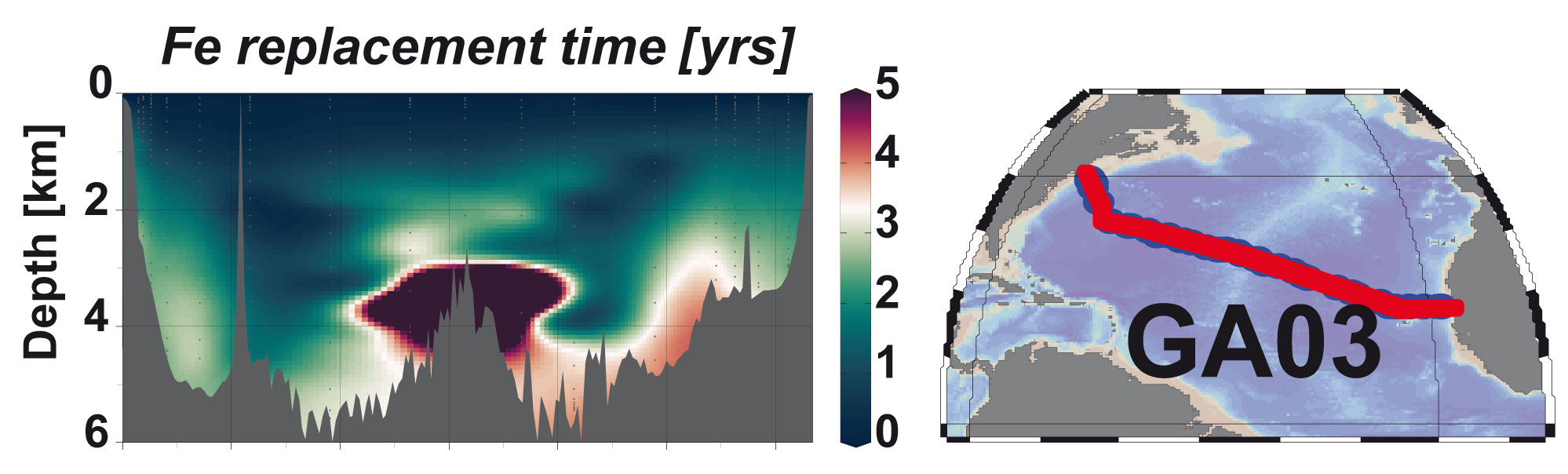
Figure: (Left) Replacement time of dissolved Fe across the GEOTRACES cruise section GA03. This replacement time is how long it would take to replace all of the iron in the North Atlantic Ocean with a source of iron derived from the quantifiable delivery of the crustal isotope thorium-232 to the ocean. (Right) Map showing the GEOTRACES section GA03 in the Atlantic Ocean. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Hayes, C. T., Anderson, R. F., Cheng, H., Conway, T. M., Edwards, R. L., Fleisher, M. Q., Ho, P., Huang, K.-F., John, S., Landing, W.M., Little, S. H. Lu, Y., Morton, P. L., Moran, S. B., Robinson, L. F., Shelley, R. U., Shiller, A. M., Zheng, X.-Y. (2018). Replacement Times of a Spectrum of Elements in the North Atlantic Based on Thorium Supply. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 32(9), 1294–1311. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1029/2017GB005839
You can also read the Research Spotlight about this paper published on Eos.org: https://eos.org/research-spotlights/a-novel-approach-reveals-element-cycles-in-the-ocean
