Methylmercury subsurface maxima explain mercury accumulation in Canadian Arctic marine mammals
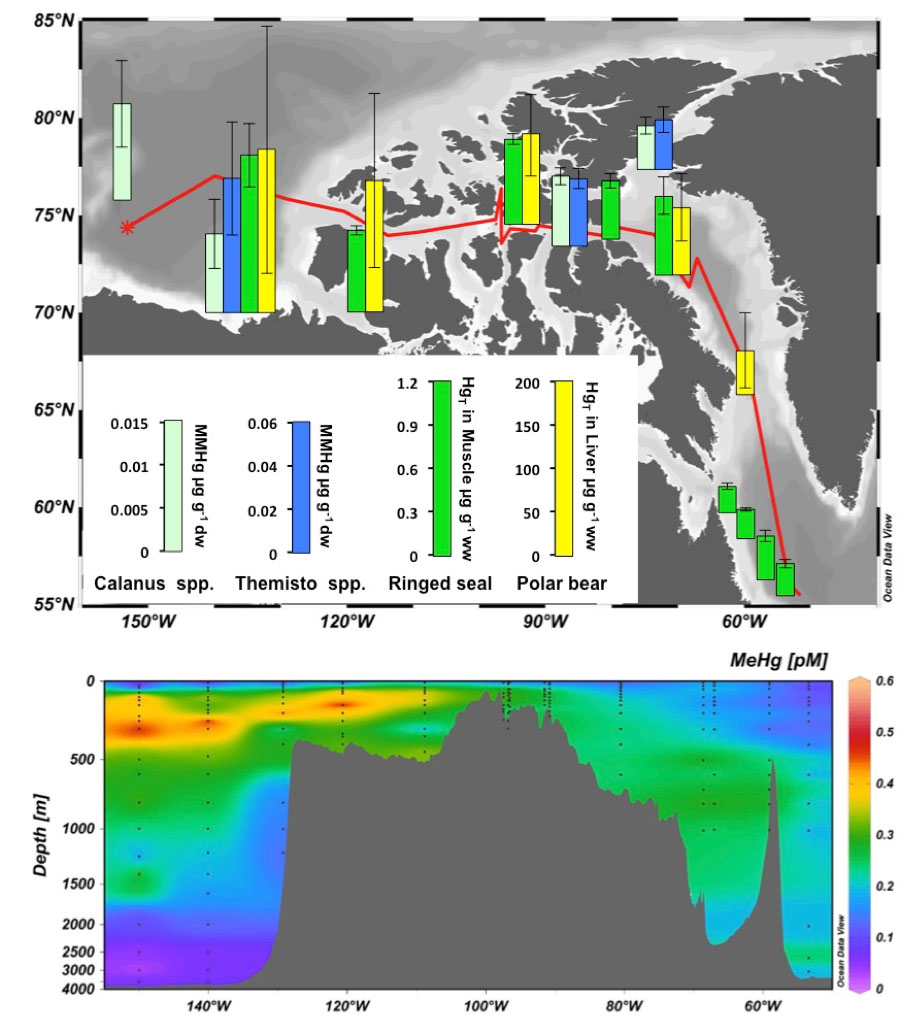
Mercury (Hg) concentrations in Canadian Arctic marine mammals were monitored during the last four decades and found to be highly elevated, frequently exceeding toxicity thresholds. Mercury concentrations in marine biota are also found to be generally higher in the western part of the Canadian Arctic than in the east. Thanks to the Canadian Arctic GEOTRACES cruise, Wang and co-authors (2018, see reference below) carried out a high-resolution total mercury and methylmercury (MeHg) measurements from the Canada Basin in the west to the Labrador Sea in the east. Total Hg concentrations show a distinctive longitudinal gradient along the transect with concentrations increasing from the Canada Basin eastward through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago to Baffin Bay, which is opposite to the spatial gradient in mammal Hg.
What is remarkable is the distribution patterns of MeHg. The authors found that MeHg concentrations are lowest at the surface, peak in a subsurface layer (~100–300 m), and subsequently decrease towards the bottom. Longitudinally, the subsurface MeHg peak value is highest in the western part of the section and decreases towards the east, eventually reaching its lowest values in the Labrador Sea. Given that it is MeHg that accumulates and biomagnifies in marine biota and that the MeHg subsurface maxima lie within the depths where Arctic marine biota reside, this gradient readily explains the spatial distribution of Hg levels observed in Canadian Arctic mammals.
Elucidating the processes that generate and maintain this subsurface MeHg maximum is the next challenge…
Reference:
Wang, K., Munson, K. M., Beaupré-Laperrière, A., Mucci, A., Macdonald, R. W., & Wang, F. (2018). Subsurface seawater methylmercury maximum explains biotic mercury concentrations in the Canadian Arctic. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 14465. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32760-0
