Cadmium to phosphorus ratio in euphotic zone particulates: why does it vary?
Bourne and co-workers examine the particulate cadmium to phosphorus ratio (Cd/P) variations of 3 particle fractions (<1µm, 1-51µm and >51µm) from 50 casts covering spatial and temporal scales never reached so far for these parameters. This impressive data set allows them to study the effects of an El Niño, upwelling, large-scale in situ Fe fertilization, low-oxygen conditions, and seasonal variation on the cadmium to phosphorus (Cd:P) in particles. The authors found seasonal and spatial variation over an order of magnitude in particulate Cd:P ratios. They figure out that Cd:P tends to be higher (~1–2 mmol/mol) in particles gathered in biologically dynamic waters and is much lower (typically ~0.1 mmol/mol) in oligotrophic regions. Using a statistical approach, they find that 3 factors—local dissolved nitrate, silicate concentrations, and euphotic zone depth—can predict 59% of the variation in particulate Cd:P.
GEOTRACES GP15, at sea from September through November 2018 will collect size fractionated particulates along the 152W meridian from the Aleution Islands to Tahiti. In the future, Bourne et al. hope to use Cd:P data from those particles to compare to their predictions.
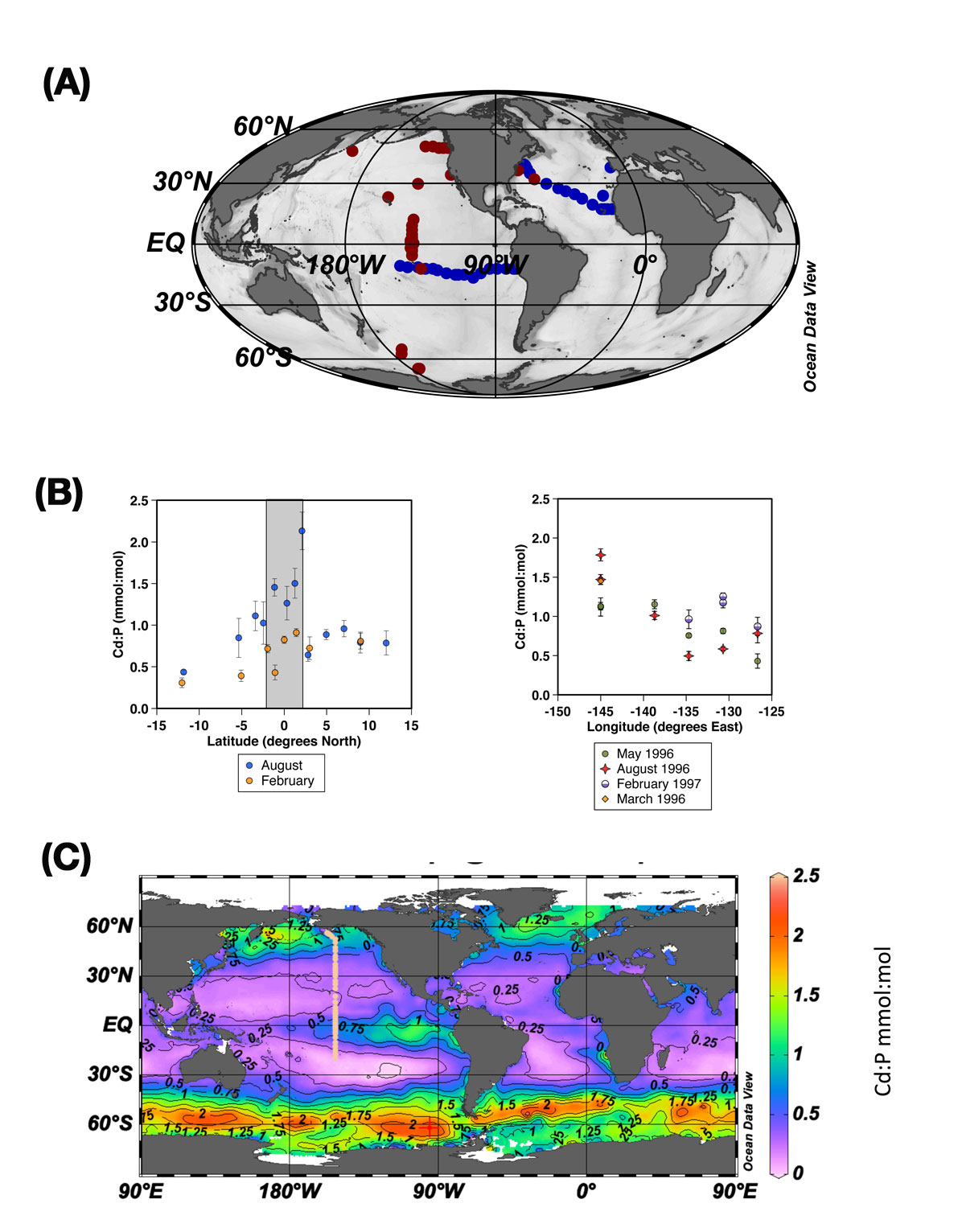
Figures: (A) Map of sample locations. Samples collected using the Multiple Unit Large Volume Filtration System are marked in maroon. Samples collected during GEOTRACES GA03 and GP16 are marked in dark blue.
(B) Left: Euphotic zone average Cd:P in combined <1 and 1-51 μm particles collected during two US-JGOFS Equatorial Pacific cruises in February and August 1992. Blue circles represent the August 1992 cruise when typical upwelling conditions were present. Orange circles represent the February 1992 cruise during El Nino conditions.
(B) Right: Euphotic zone average Cd: P values along Line P from four cruises in the combined <1 and the 1-51 μm size fractions. Different shapes represent the different seasons. Day and night profiles were taken at OSP during the May and August 1996 cruises [Bishop et al., 1999].
(C) Seasonal euphotic zone particulate Cd:P prediction for fall (September, October, November). Peach dots represent stations in current GP15 cruise.
Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Bourne, H. L., Bishop, J. K. B., Lam, P. J., & Ohnemus, D. C. (2018). Global Spatial and Temporal Variation of Cd:P in Euphotic Zone Particulates. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 32(7), 1123–1141. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1029/2017GB005842
Bishop, J. K. B., Calvert, S. E., & Soon, M. Y. S. (1999). Spatial and temporal variability of POC in the northeast subarctic Pacific. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 46(11–12), 2699–2733. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0645(99)00081-8
