When direct mapping of diatoms reveals unexpected fate of trace metals in the twilight zone
Twining and co-authors (2014, see reference below) used synchrotron x-ray fluorescence mapping to measure macronutrients such phosphorus (P), sulphur (S), and silicon (Si), and also trace metals like iron (Fe), nickel (Ni) and zinc (Zn), in individual cells of a diatom specie during a spring bloom off New Zealand. They clearly show that P, S, Zn and Ni are released faster than Fe and Si from sinking cells in the upper 200 m. Although the metals are co-located with P and S at the surface, the scheme changes deeper. The relationships with P and S become weak while an association of Fe with Si appears, suggesting re-adsorption when particles are settling. Exciting results revealing that ratios of dissolved Fe to macronutrients in the water column likely underestimate stoichiometries in sinking cells.
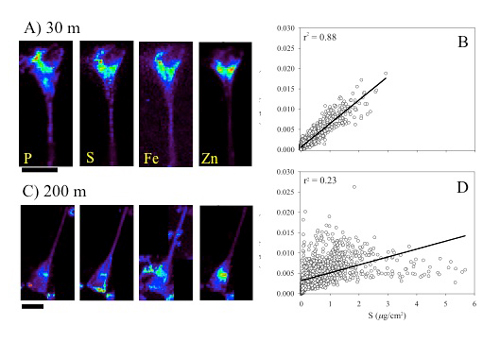
Figure. Element maps (P, S, Fe ,and Zn) and associated scatterplots of Fe and S concentrations in each pixel of the scans for two diatom cells collected from 30m or 200m following a spring bloom off New Zealand. The scatterplots show that Fe and S are spatially decoupled from each other when the diatom cells degrade as they sink through the upper water column. S is lost more readily from the cells, while Fe appears to be retained or is re-scavenged. Scale bar indicates 10um for each cell. Adapted from Twining et al. (2014). Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Twining, B. S., Nodder, S. D., King, A. L., Hutchins, D. A., LeCleir, G. R., DeBruyn, Jennifer M.; Maas, E. W., Vogt, S., Wilhelm, S. W., Boyd, P. W. (2014). Differential remineralization of major and trace elements in sinking diatoms. Limnology and Oceanography, 59(3), 689–704. doi:10.4319/lo.2014.59.3.0689 Click here to view the paper.
