Using chromium isotopes to reconstruct the oxygenation history of the oceans is challenged by modern data
Analyses of seawater chromium (Cr) concentrations and isotopes in diverse marine environments (Arctic, Pacific, and Atlantic Oceans) reveal a strong correlation between Cr isotope composition (δ53Cr) and Cr concentration. High δ53Cr values and low Cr concentration reflect losses of isotopically light Cr in neritic environments. Contrastingly, open ocean waters with low δ53Cr values and high Cr concentration are hypothesized to reflect the addition of seawater-derived Cr released from marine sediments or settling particles. Although reductive removal of Cr in oxygen minimum zones (OMZs) may explain low Cr concentrations in subsurface north Pacific waters, the heterogeneity in δ53Cr values in the modern (oxic) ocean entails that redox cycling of Cr isotopes in the ocean should be considered in future research.
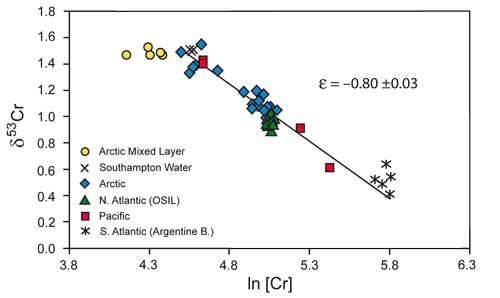 Figure: Correlation between chromium concentration (as ln[Cr]) and δ53Cr (‰) illustrates that samples from several locations around the world plot on a line that is consistent with closed-system Raleigh fractionation. This fractionation is probably the result of reduction of Cr(VI) is shallow and surface waters, and oxygen minimum zones, and possible reoxidation of Cr(III) at depth; observationally, Cr is “added” at depth, resulting in higher concentrations and lower δ53Cr values, and is “removed” in the surface, resulting in lower concentrations and higher d53Cr values. Click here to view the figure larger.
Figure: Correlation between chromium concentration (as ln[Cr]) and δ53Cr (‰) illustrates that samples from several locations around the world plot on a line that is consistent with closed-system Raleigh fractionation. This fractionation is probably the result of reduction of Cr(VI) is shallow and surface waters, and oxygen minimum zones, and possible reoxidation of Cr(III) at depth; observationally, Cr is “added” at depth, resulting in higher concentrations and lower δ53Cr values, and is “removed” in the surface, resulting in lower concentrations and higher d53Cr values. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Scheiderich, K., Amini, M., Holmden, C., & Francois, R. (2015). Global variability of chromium isotopes in seawater demonstrated by Pacific, Atlantic, and Arctic Ocean samples. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 423, 87–97. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2015.04.030
