Unique winter dataset of particulate and dissolved cadmium in the Indian sector of the Southern Ocean
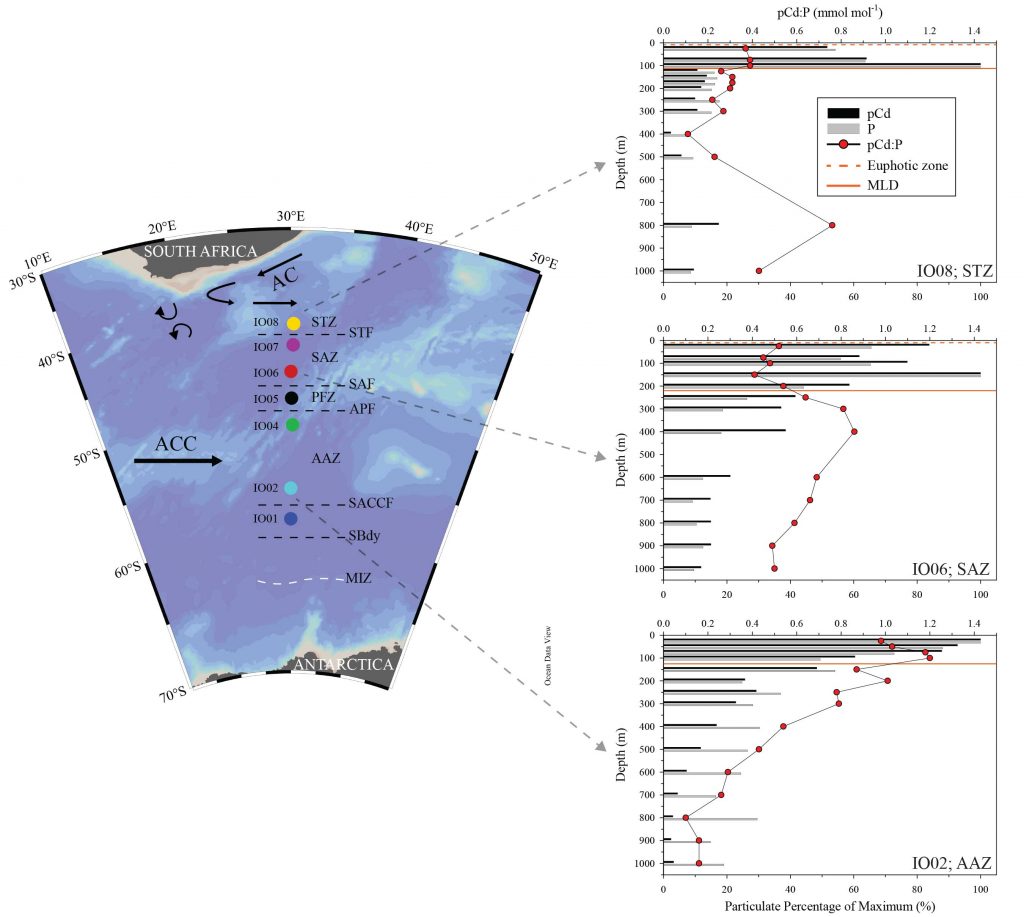
Cloete and collaborators (2021, see reference below) analysed particulate and dissolved cadmium (pCd and dCd respectively) at 7 stations in austral winter along a North South section between 41°S and 58°S, off South Africa. This heroic sampling effort and the subsequent analyses allowed these authors to establish that: 1) biological activity was still ongoing in winter although weaker than in summer; 2) biologically driven particulate Cd/P variations were observed along the section reflecting a stronger demand of Cd by diatoms in the Antarctic Zone compared to surface waters to the North; 3) the uptake of Cd is driven predominantly by the availability of dCd as well as a complex interplay involving dissolved iron (dFe), zinc (dZn) and manganese (dMn).
This last observation leads to distinct regional trends in Cd (vs phosphate, P) uptake and remineralization. The authors discuss the implications of the differential particulate Cd and P remineralization for the dCd to PO4 ratios in the upper water column. They also identify that in intermediate and deep waters, dCd distributions are largely the result of mixing between northward traveling waters of Antarctic origin (high dCd/dPO4 signatures) and southward traveling North Atlantic Deep Water (low dCd/dPO4 signature).
Reference:
Cloete R, Loock JC, van Horsten NR, Fietz S, Mtshali TN, Planquette H and Roychoudhury AN (2021) Winter Biogeochemical Cycling of Dissolved and Particulate Cadmium in the Indian Sector of the Southern Ocean (GEOTRACES GIpr07 Transect). Front. Mar. Sci. 8:656321. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.656321
