Trace metals in deep ocean waters: A review
A synthesis on the data available on the distribution of selected trace metals (i.e. Cadmium, Cobalt, Copper, Molybdenum, Nickel, Lead and Zinc) in the deep ocean from 1979 to 2009 is provided by Aparicio-González and colleagues (Aparicio-González et al., 2012). This article also identifies patterns as well as gaps in currently available data in terms of their capacity to depict their global distributions.
A great contribution for the GEOTRACES Programme !
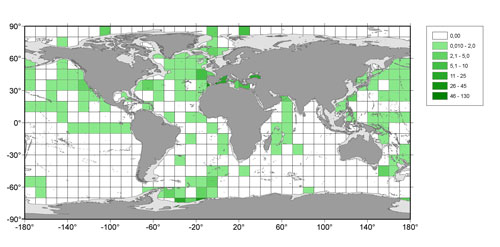
Figure: Geographic location of reported depth profiles (1000 m or deeper) for all studied elements together, as of 1976 to 2009. Colors scale indicates the number of deep profiles per 100,000 km2. Source: Journal of Marine Systems
Reference:
Aparicio-González A., Duarte CM., Tovar-Sánchez A. (2012), Trace metals in deep ocean waters: A review, Journal of Marine Systems 100–101 (26-33), DOI : 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.03.008
