The power of combining geochemical tracer data with direct current measurements
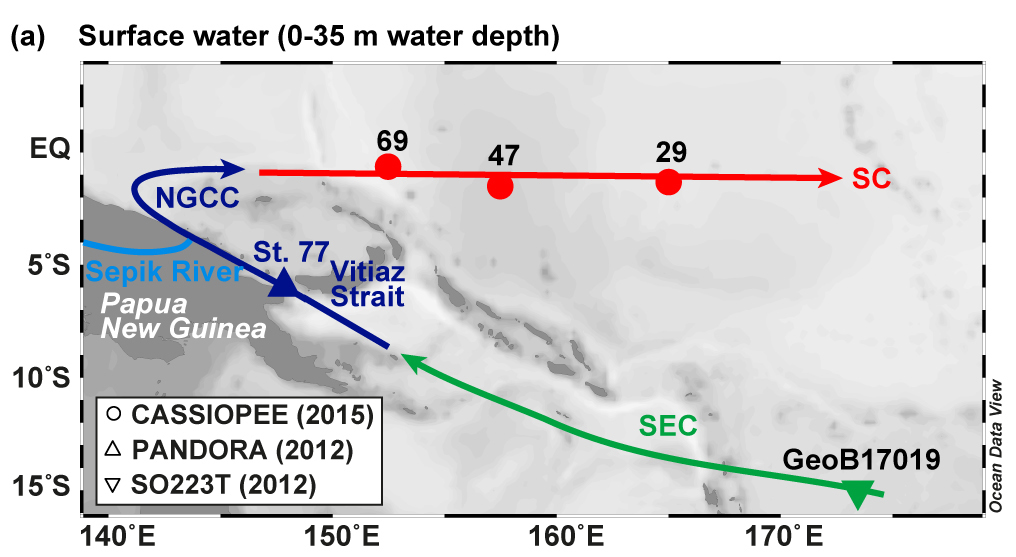
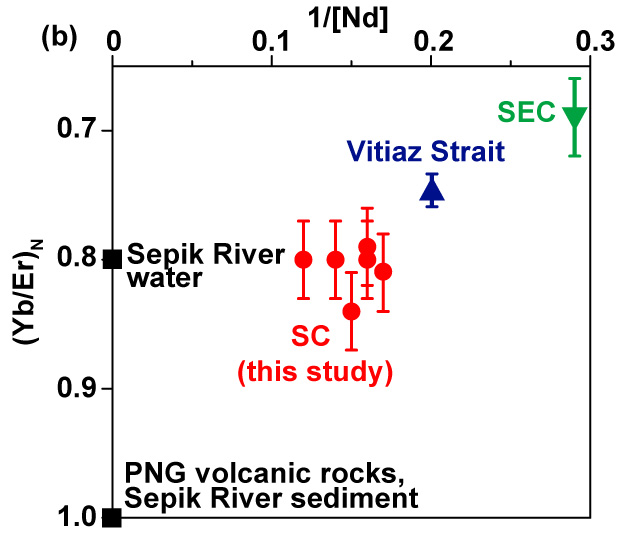
By using an original combination between seawater Rare Earth Elements (REE) concentrations and direct physical oceanographic observations (e.g., current velocity data), Behrens and collaborators (2020, see reference below) characterised the geochemical composition, origin and pathways of the complex surface and upper layer currents of the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean. They show that surface water enrichments are largely derived from the basaltic Papua New Guinea margin sediments and/or the Sepik river solid discharge, while the Sepik dissolved input represents less than 3.5% input of the neodymium flux leaving the Solomon Sea by the Vitiaz Strait. The combination also allows discussing the temporal variability of the REE sources in this area.
Reference:
Behrens, M. K., Pahnke, K., Cravatte, S., Marin, F., & Jeandel, C. (2020). Rare earth element input and transport in the near-surface zonal current system of the Tropical Western Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 549, 116496. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EPSL.2020.116496
