The potential of anthropogenic 236-Uranium as a new and transient oceanographic tracer demonstrated in the North Atlantic
236-Uranium (236U) is present on Earth due to natural and anthropogenic production. However, the estimated inventory of anthropogenic 236U (106 kg) largely exceeds the natural one (30 kg). Releasing even a tiny fraction of this artificial isotope would drastically change the environmental 236U/238U ratio and therefore make this ratio a useful isotopic marker to trace such anthropogenic releases and to study seawater transport and mixing processes in the ocean.
Casacuberta and her colleagues took this premise to propose the first transect of 236U in the North Atlantic Ocean during the first two legs of the GEOTRACES GA02 cruise. Global fallout and the releases of the European reprocessing nuclear plants La Hague and Sellafield are the main sources of 236U to the ocean. Results of this transect showed that there is a North to South and surface to deep decreasing gradient of 236U/238U atomic ratio when moving from 64ºN to 2ºN mirroring the distribution of waters masses in this region. In particular, highest 236U contents are shown in the Labrador Sea Water and Denmark Strait Overflow Water, tracing the penetration of waters to the North Atlantic Ocean that carry the signal of 236U from the two European reprocessing plants. This pioneer work is proving that 236U can be an efficient water mass transient tracer.
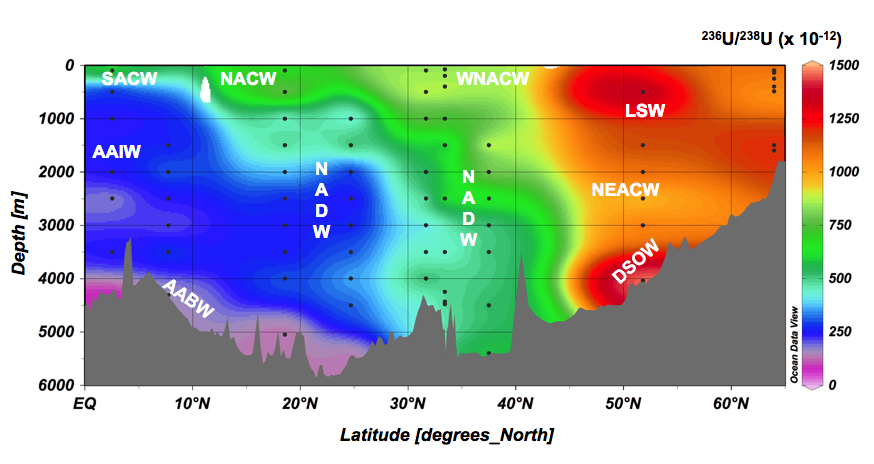
Figure: Distribution of 236U in the North Atlantic Ocean. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Casacuberta, N., Christl, M., Lachner, J., Rutgers van der Loeff, M., Masqué, P., & Synal, H. -A. (2014). A first transect of 236U in the North Atlantic Ocean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 133, 34–46. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.02.012. Click here to access the paper.
