The Colloidal Hourglass: North Atlantic Iron Distribution Controlled by Dynamic Colloidal Phase
K. Kunde and colleagues (2019, reference below) show that a highly dynamic colloidal iron phase in the upper ocean and at the seafloor boundary controls the distribution of dissolved iron at key sources and sinks across the subtropical North Atlantic Ocean, while the ocean interior is marked by an equilibrium partitioning between the soluble and colloidal phases. These processes result in size-fractionated iron distribution resembling an hourglass shape of the colloidal iron fraction (%cFe) of the dissolved pool against depth. In addition, high-resolution surface sampling revealed a strong, dust-derived gradient of surface dissolved iron concentrations that resulted in a “high dust, high %cFe” and “low dust, low %cFe” pattern across the basin. A global comparison of colloidal and dissolved iron reveals that this effect extends to the mesopelagic, where the lithogenic nature of a region is imprinted on the colloidal partitioning signature.
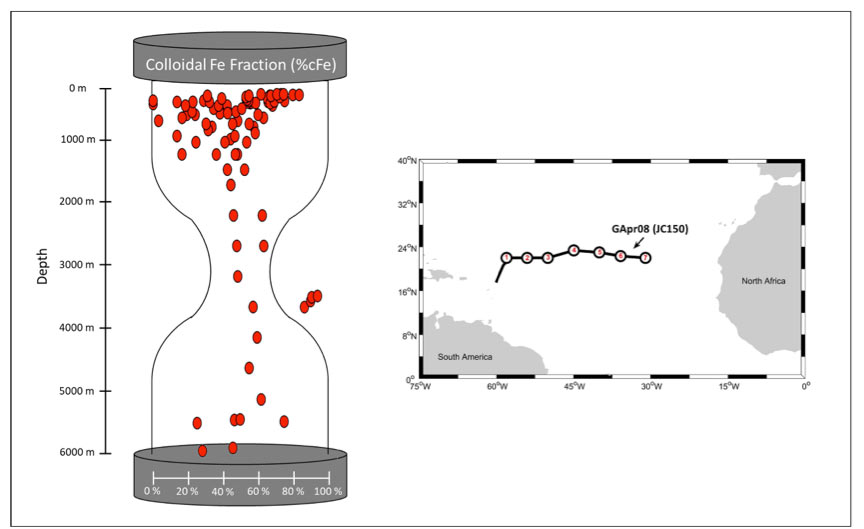
Figure: (Left) The fraction of colloidal Fe to the dissolved Fe pool across the GApr08 section forms an hourglass shape against depth. Dynamic Fe cycling in the upper ocean and near the seafloor is reflected in the large range of %cFe, while the tight partitioning in the less dynamic ocean interior forms the neck of the hourglass. The four data points outside this pattern are from the Snakepit hydrothermal source on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (Station 4) with almost 100% cFe. (Right) Map of the subtropical North Atlantic showing the cruise track and station locations of the GApr08 section (research cruise JC150).
Reference:
Kunde, K., Wyatt, N. J., González‐ Santana, D., Tagliabue, A., Mahaffey, C., & Lohan, M. C. (2019). Iron distribution in the subtropical north Atlantic: the pivotal role of colloidal iron. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 33, 1532 1547. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GB006326
