Surprisingly heavy silicon isotopes in the surface and deep Arctic Ocean
The silicon isotopic composition of any oceanic water body results from an interplay between silicic acid (Si(OH)4) sources, its physical transport and the biological fractionation. Brzezinski and his colleagues (2021, see reference below) report on a comprehensive study of the Arctic Ocean Si(OH)4 concentrations and Si isotopic composition based on the analysis of a large set of GEOTRACES GN01 cruise samples together with the comparison with previous data sets. They found:
- Anomalously heavy isotopes (d30Si(OH)4 up to +3.2 ‰) together with high Si(OH)4 concentrations characterise the surface waters along the transpolar drift (TPD). This reflects both the influence of the high silicate content of riverine source waters and the strong biological Si(OH)4 consumption on the Eurasian shelves.
- The highest Si(OH)4 concentrations are observed deeper, in the complex halocline system found in the Canadian basin, while the Si isotopes show a minimum. High-[Si(OH)4] Pacific source waters and benthic inputs of Si(OH)4 in the Chukchi Sea likely explain this contrast.
- Finally, intermediate and deep waters display an increase of the [Si(OH)4] concentrations concomitant to a progressive decrease of the d30Si(OH)4 values. Still, these intermediate and deep waters remain heavier than deep waters from other oceanic basins.
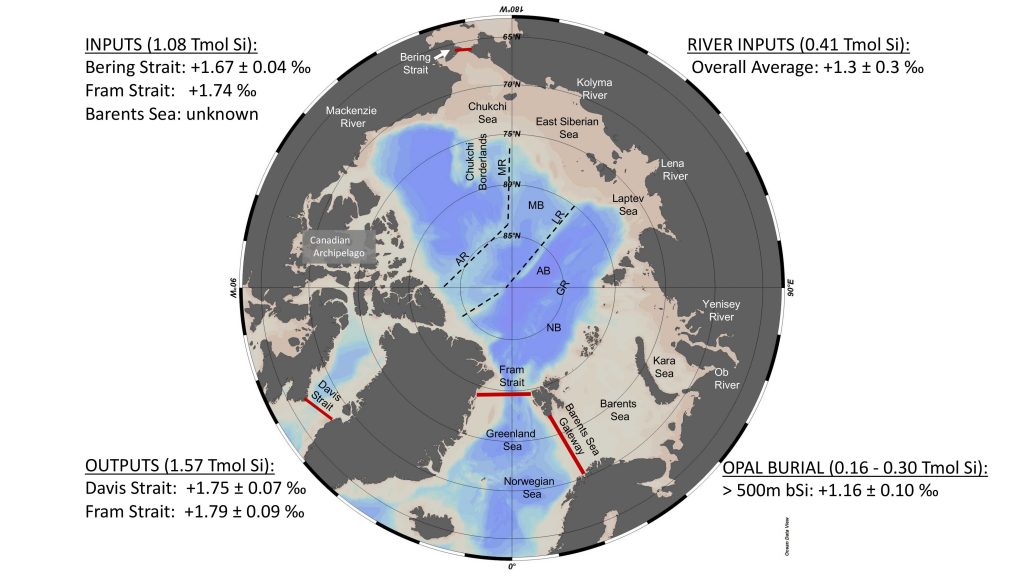
The authors propose a budget of both parameters for the Arctic Ocean, revealing nearly identical isotope values for seawater inflows and seawater outflows despite a significant inflow of light isotopes of Si from rivers (see figure below). That imbalance implies a previously unrecognized role of biological fractionation and the burial of isotopically light opal as a sink of light isotopes in the Arctic Si isotope budget.
Reference:
Brzezinski, M. A., Closset, I., Jones, J. L., de Souza, G. F., & Maden, C. (2021). New Constraints on the Physical and Biological Controls on the Silicon Isotopic Composition of the Arctic Ocean. Frontiers in Marine Science, 8, 931. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.699762
Torres-Valdés, S., Tsubouchi, T., Bacon, S., Naveira-Garabato, A. C., Sanders, R., McLaughlin, F. A., et al. (2013). Export of nutrients from the Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 118, 1625–1644. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrc.20063
