Surprise in the Gulf of Aqaba: intense dust inputs are not a source of trace metals to seawater!
Catching the impact of short-term environmental perturbations such as dust storms and sediment resuspension events on the oceanic water column is always a main challenge. Time Series Stations (TSS) are good tools to improve the temporal sampling resolution allowing the description of episodic natural events and their impact on the water column.
Benaltabet and his colleagues (2023, see reference below) present a 2-year time series of dissolved manganese, cobalt, nickel, copper, zinc, cadmium, and phosphate concentration profiles sampled at a daily resolution in the Gulf of Aqaba (GoA), Red Sea. The characteristics of this TSS is to provide a highly accessible deep oligotrophic water body, experiencing intensive atmospheric and resuspension events.
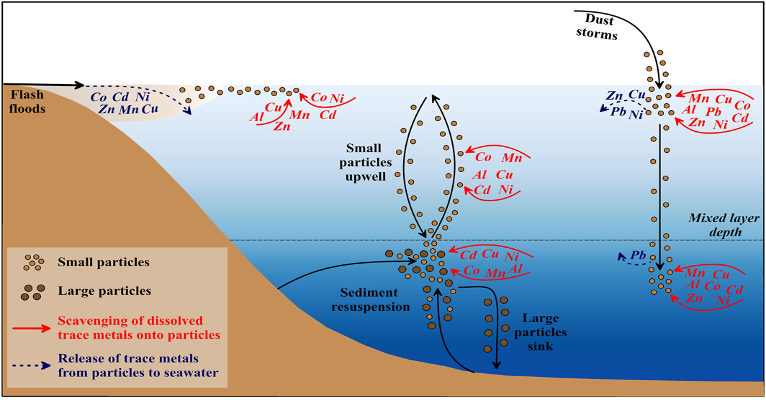
Their main results are that 1) upper water column trace metal inventories decrease with increasing dust loads. Aerosol-induced shifts peak ∼5–6 days after dust deposition and 2) dust storms and sediment resuspension events drive a decrease in trace metal (manganese, cobalt, nickel, copper and cadmium) concentrations.
These results are surprising and reflect a process of metal adsorption onto dust particles sinking in seawater (scavenging). These unique findings allow the authors to quantify the impacts of dust on seawater trace metal contents, and demonstrate that on the long term, dust is a source of metals to the oceans, but on shorter time scales, dust is also capable of removing metals from seawater.
References:
Benaltabet, T., Lapid, G., & Torfstein, A. (2023). Response of Dissolved Trace Metals to Dust Storms, Sediment Resuspension, and Flash Floods in Oligotrophic Oceans. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 37. Access the paper:10.1029/2023gb007858
Benaltabet, T., Lapid, G., & Torfstein, A. (2022). Dissolved aluminium dynamics in response to dust storms, wet deposition, and sediment resuspension in the Gulf of Aqaba, northern Red Sea. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 335, 137–154. Access the paper: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.08.029
Benaltabet, T., Lapid, G., & Torfstein, A. (2020). Seawater Pb concentration and isotopic composition response to daily time scale dust storms in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Marine Chemistry, 227, 103895. Access the paper: 10.1016/j.marchem.2020.103895
