Strong lithogenic imprints in the Indian Ocean waters
Ueki and co-authors (2024, see reference below) reported the first sectional distributions of zirconium (Zr), hafnium (Hf), and niobium (Nb) along a north-south track in the Indian Ocean (Japanese cruise on R/V Hakuho Maru along GEOTRACES GI04 section). They discuss their results also considering the orthosilicic acid, Si(OH)4, aluminum (Al) and neodymium- Neodymium isotope composition (Nd-EpsNd) distributions. Interesting features are:
- That the concentrations of dZr and dHf in the deep waters of the Indian Ocean were higher than those in the North Pacific Ocean, which differs from conventional nutrient-type elements such as Si.
- dZr and dHf distribution, at the surface as in deeper Indian Ocean layers, are strongly reflecting lithogenic inputs. The consistency of their distributions with the dAl one confirms that Al is a good proxy for incompatible elements.
- In waters deeper than 1400m, the dZr/dHf ratio increased along the thermohaline circulation. This reflects the preferential removal of dHf over dZr along the conveyor belt together with the strong lithogenic supply in the Indian Ocean. Such observation leads the authors to propose that dissolved Zr/Hf molar ratio is promising as a tracer for global ocean circulation, more specifically to discriminate better the Indian and Pacific deep waters.
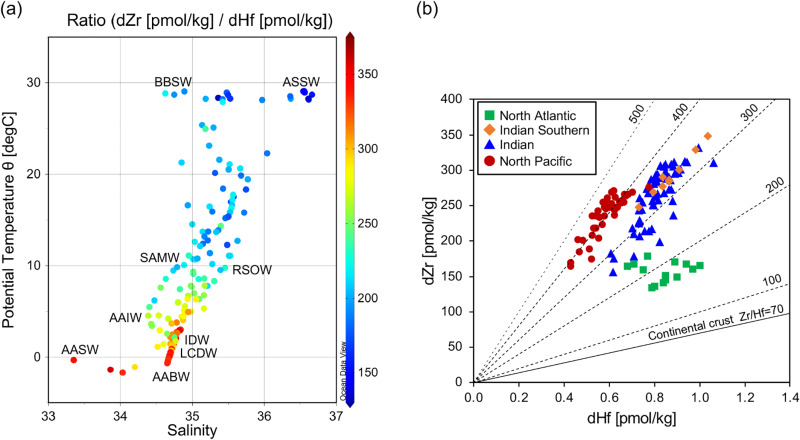
(Figure 2a) T-S diagram in this study. The dot colour represents the dZr/dHf mole ratio. ASSW: Arabian Sea Surface Water, BBSW: Bay of Bengal Surface Water, RSOW: Red Sea Overflow Water, AASW: Antarctic Surface Water, SAMW: Subantarctic Mode Water, AAIW: Antarctic Intermediate Water, IDW: Indian Deep Water, LCDW: Lower Circumpolar Deep Water, AABW: Antarctic Bottom Water.
(Figure 2b) Plots of dZr versus dHf in deep water (< 1400 m) of the North Atlantic Ocean (Godfrey et al., 1996), the Indian sector of the Southern Ocean (this study; ER14), the Indian Ocean (this study; ER2–12), and the subarctic North Pacific Ocean (Tanaka et al., 2019; Ueki et al., 2023). The broken lines show Zr/Hf mole ratio. The solid line shows Zr/Hf mole ratio in the continental crust (Rudnick et al., 2003).
References:
Ueki, R., Zheng, L., Takano, S., & Sohrin, Y. (2024). Distributions of zirconium, hafnium, and niobium in the Indian Ocean: Influence of lithogenic sources on incompatible elements. Marine Chemistry, 260, 104365. Access the paper: 10.1016/j.marchem.2024.104365
Godfrey, L. V., White, W. M., & Salters, V. J. M. (1996). Dissolved zirconium and hafnium distributions across a shelf break in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(21), 3995–4006. Access the paper: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00246-3
Tanaka, Y., Tsujisaka, M., Zheng, L., Takano, S., & Sohrin, Y. (2019). Application of NOBIAS Chelate-PA 1 Resin to the Determination of Zirconium, Niobium, Hafnium, and Tantalum in Seawater. Analytical Sciences, 35(9), 1015–1020. Access the paper: 10.2116/analsci.19P069
Rudnick, R. L., & Gao, S. (2003). Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry (pp. 1–64). Elsevier. Access the paper: 10.1016/B0-08-043751-6/03016-4
