Present day neodymium isotopic composition of the Caribbean Sea deep waters questions the paleo-application of this tracer in restricted basins
The first profiles of neodymium (Nd) concentration and isotopic composition in the Carribbean Sea have been published. They show that surface and intermediate waters flow through the Caribbean with essentially unchanged Nd isotopes ratios (εNd), whereas deep waters are strongly modified. Indeed, they likely receive radiogenic Nd released from the local sediments, of volcanic origin. Osborne and co-authors (2014, see reference below) suggest that this important shift is facilitated by the long residence time of these deep waters (150 years). This finding has general implications for paleoceanographic studies in restricted basins, where the composition of seawater is sensitive to its residence time within the basin.
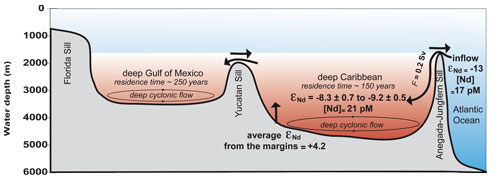
Figure. Schematic cross-section of the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico basins, showing the Nd isotopic composition and concentration of inflowing Atlantic water and how it changes to more radiogenic compositions and higher concentrations within the deep Caribbean. Interaction of seawater with radiogenic Nd from the margins of the Caribbean may be responsible for this change, aided by the slow replenishment rate and long residence time of deep waters in the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference :
Osborne, A. H., Haley, B. A., Hathorne, E. C., Flögel, S., & Frank, M. (2014). Neodymium isotopes and concentrations in Caribbean seawater: Tracing water mass mixing and continental input in a semi-enclosed ocean basin. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 406, 174–186. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2014.09.011 Click here to access the paper.
