Organic copper complexation may stabilise seawater stable copper isotopic composition
Three deep-sea profiles were produced for the analysis of copper (Cu) concentration, along a transect covering very different biogeochemical regions: the oligotrophic North Tasman Sea (30ºS), the Tasman Front (40°S) and the productive waters of the Southern Ocean in the south (46°S).
Despite these differences, the Cu isotope composition of all three profiles was relatively homogenous. This homogeneity is attributed to the fact that more than 99% of the Cu is organically complexed, measured as part of the same study (Thompson et al, 2014; see references below). It is therefore argued that organic complexation stabilises heavy values of seawater stable copper isotopic composition (δ65Cu).
The authors also propose that decomposition of organic Cu complexes in environments such as anoxic basins may provide an isotopically heavy source of Cu for further scavenging and/or removal to the sediments. Such mechanism would help to balance the oceanic budget of δ65Cu, discussed in Little et al, 2014 (see reference below, and GEOTRACES science highlight).
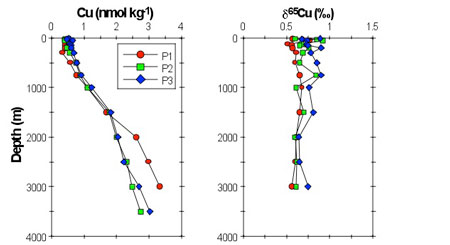
Figure: Three dissolved copper concentration profiles versus depth (left panel) along with the isotope composition for dissolved copper (right panel). Samples were collected from three stations (P1, P2 and P3) occupied in the Tasman Sea region.
References :
Little, S. H., Vance, D., Walker-Brown, C., & Landing, W. M. (2014). The oceanic mass balance of copper and zinc isotopes, investigated by analysis of their inputs, and outputs to ferromanganese oxide sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 125, 673–693. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2013.07.046 Click here to acces the paper.
Thompson, C.M., Ellwood, M.J., Sander, S.G., (2014). Dissolved copper speciation in the Tasman Sea, SW Pacific Ocean. Marine Chemistry, 164: 84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.06.003 Click here to access the paper.
Thompson, C.M., Ellwood, M.J., (2014). Dissolved copper isotope biogeochemistry in the Tasman Sea, SW Pacific Ocean. Marine Chemistry, 165: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.06.009 Click here to access the paper.
