On the optimal use of the seaFAST system
Do you wish to improve your recoveries, blanks or any other parameter of your seawater preconcentration system (seaFAST)? Or are you simply curious about it? Wuttig and co-workers (2019, see reference below) propose a critical evaluation of this system’s capabilities. They perform an impressive list of tests including system conditioning, improving blank levels, finding the optimal pH of the buffer, improving preconcentration factors for different sample matrices, estimating memory effects, the initial sample salinity and UV oxidation effects on trace element concentrations. These tests considered an array of trace elements (cadmium, cobalt, copper, iron, gallium, manganese, nickel, lead, titanium and zinc) using SF-ICP-MS with data validation for some of these trace elements by flow injection analysis (iron, manganese) and/or GEOTRACES (n=42 for GSP and GSC) reference samples. They eventually make a long and useful list of recommendations for an optimal use of the system.
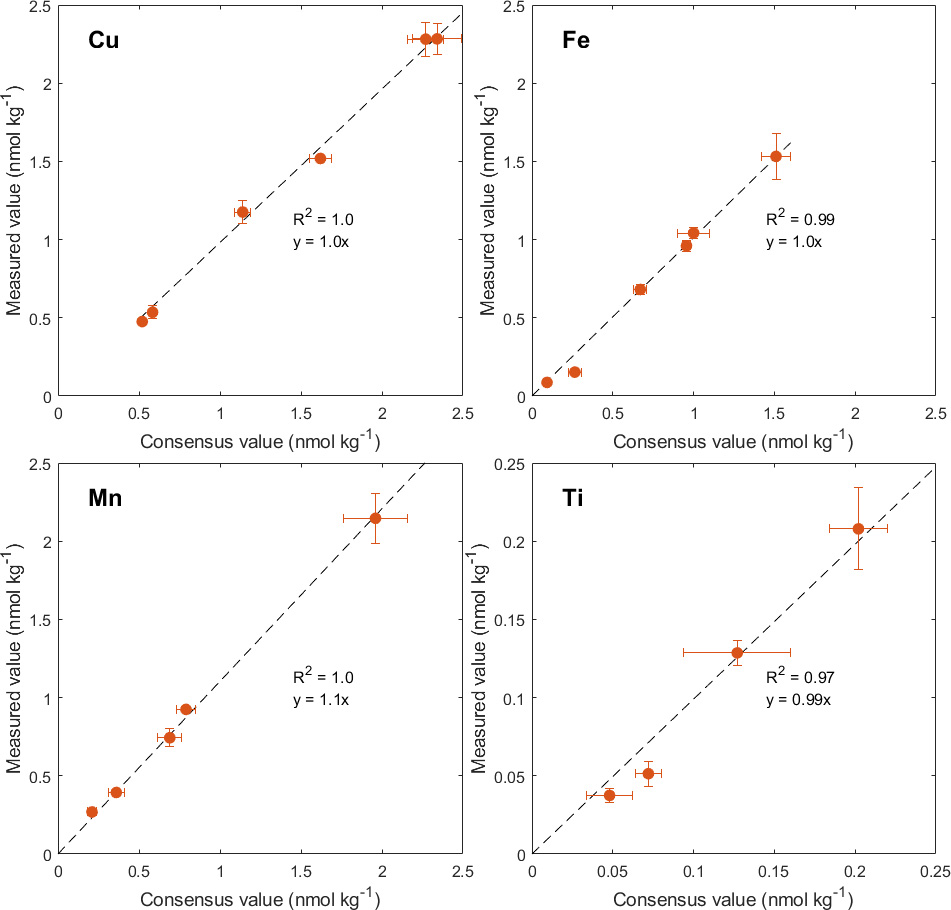
Figure: During this work, a commercially available seaFAST preconcentration system combined with sector-field inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SF-ICP-MS) was utilised to measure six reference seawaters (SAFe S, D1 and D2; GEOTRACES GD, GSC and GSP) 3-42 times each. In this figure, our measured values were compared to the consensus values for copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn) and Titanium (Ti). Titanium is a novel element for this system with limited consensus values available and was compared to values determined with voltammetry by Croot, 2011. Errors are presented as 1 standard deviation (σ) for both consensus and the measured values. Note different scales for Ti.
Reference:
Wuttig, K., Townsend, A. T., van der Merwe, P., Gault-Ringold, M., Holmes, T., Schallenberg, C., Latour, P., Tonnard, M., Rijkenberg, M. J.A., Lannuzel, D., Bowie, A. R. (2019). Critical evaluation of a seaFAST system for the analysis of trace metals in marine samples. Talanta, 197, 653–668. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2019.01.047
Croot, P.L., Rapid determination of picomolar titanium in seawater with catalytic cathodic stripping voltammetry, Anal Chem 83(16) (2011) 6395-400.
