Ocean margins: the missing term for oceanic element budgets?
 Jeandel, Catherine, Peucker-Ehrenbrink, Bernhard, Jones, Morgan T., Pearce, Christopher R., Oelkers, Eric H., Godderis, Yves, Lacan, François, Aumont, 0livier and Arsouze, Thomas
Jeandel, Catherine, Peucker-Ehrenbrink, Bernhard, Jones, Morgan T., Pearce, Christopher R., Oelkers, Eric H., Godderis, Yves, Lacan, François, Aumont, 0livier and Arsouze, Thomas
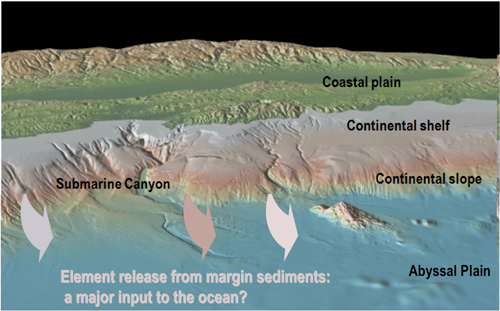
This paper underlines how poor is our understanding of the land-to-ocean element flux and rises the question of the “submarine weathering”. Indeed, isotopes of Nd, Si, Fe, Ra as well as REE, TDFe or Ba concentrations reveal that release from sediment deposited on oceanic margins can be a significant source for dissolved elements in seawater; processes yielding this release need to be understood (e.g: Boundary nepheloid layers could enhance it). This source, potentially important, has to be taken in account in oceanic budgets and climate models.
Eos, Vol. 92, No. 26, 28 June 2011
