Nickel bioactive role in the oceans assessed by its isotopes
Although Nickel (Ni) is identified as a co-enzyme factor for the phytoplankton development, its role as bioactive element is controversial. Among others, the fact that Ni concentrations are never totally depleted in the surface waters remains an enigma. Lemaitre and her colleagues (2022, see reference below) realized the simultaneous analysis of the dissolved Ni isotopes and concentrations in waters collected in contrasting biogeochemical provinces as part of the GEOVIDE cruise (GA01), to which they added data extracted from the GEOTRACES IDP2021. Based on this data set, incubation results from the literature and a 3D modelling of the oceanic Ni cycle, reveal a strong biogeochemical divide with Ni isotope fractionation only occurring in low latitude surface waters. Indeed, in their new North Atlantic dataset, the lowest Ni concentrations (1.8-2.6 nmol/L) and highest δ60Ni (up to +1.67) are associated with low nitrate, south of the subarctic front (SAF), contrasting with stations at latitudes north of the SAF, where no clear Ni concentrations and isotopic variations are observed while they are richer in nitrates. The authors also evidence relationships with nitrogen isotope effects in the same samples that are suggestive of a link between Ni utilization, isotope fractionation and nitrogen fixation. This leads them to ask the exciting question of a possible nickel-nitrogen co-limitation in the low latitude ocean.
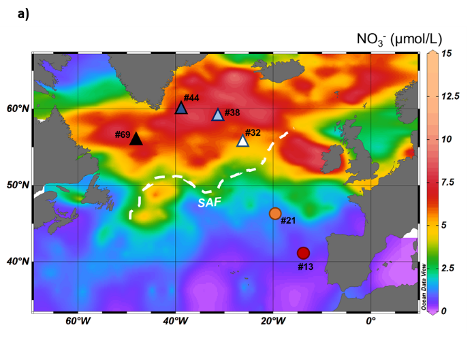
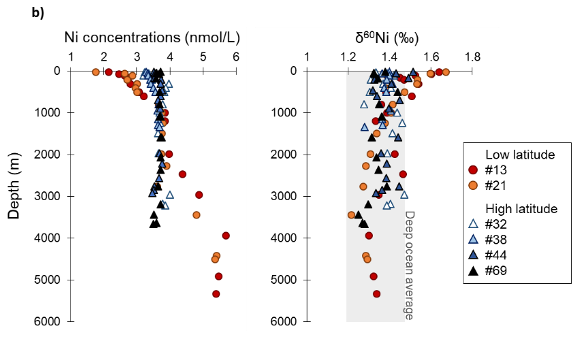
Figure: Nickel biogeochemical divide between high and low latitudes. a) Location of the GEOVIDE stations, superimposed on a map of the seasonal average nitrate (NO3–) concentrations in surface waters. The subarctic front (SAF), displayed by the white dashed line, separates the low and high latitude stations (shown as circles and triangles respectively). b) Depth profiles of dissolved Ni concentrations and isotope composition (δ60Ni) at low (shown as circles) and high (shown as triangles) latitude stations. Low Ni concentrations in surface waters of low latitude stations are accompanied by significantly higher δ60Ni values.
Reference:
Lemaitre, N., Du, J., de Souza, G. F., Archer, C., & Vance, D. (2022). The essential bioactive role of nickel in the oceans: Evidence from nickel isotopes. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 584, 117513. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2022.117513
