Neodymium concentrations and isotopes help disentangling Siberian river influences on the Arctic Ocean
Paffrath and co-autors (2021, see reference below) followed the relative contributions of the main Siberian rivers to the waters of the Transpolar Drift (TPD) using neodymium (Nd) parameters. Thanks to these river contrasting signatures (see figure 1), they could establish their lateral and vertical relative distributions as well as the spatially and temporally varying input and transport of river water constituents into and across the central Arctic Ocean. It is noted that their different densities acquired prior to incorporation into the TPD prevent mixing between the freshwater contributions. Actually, temporally varying river discharges and changing wind patterns are likely triggering lateral separation of these river influence on the TDP.
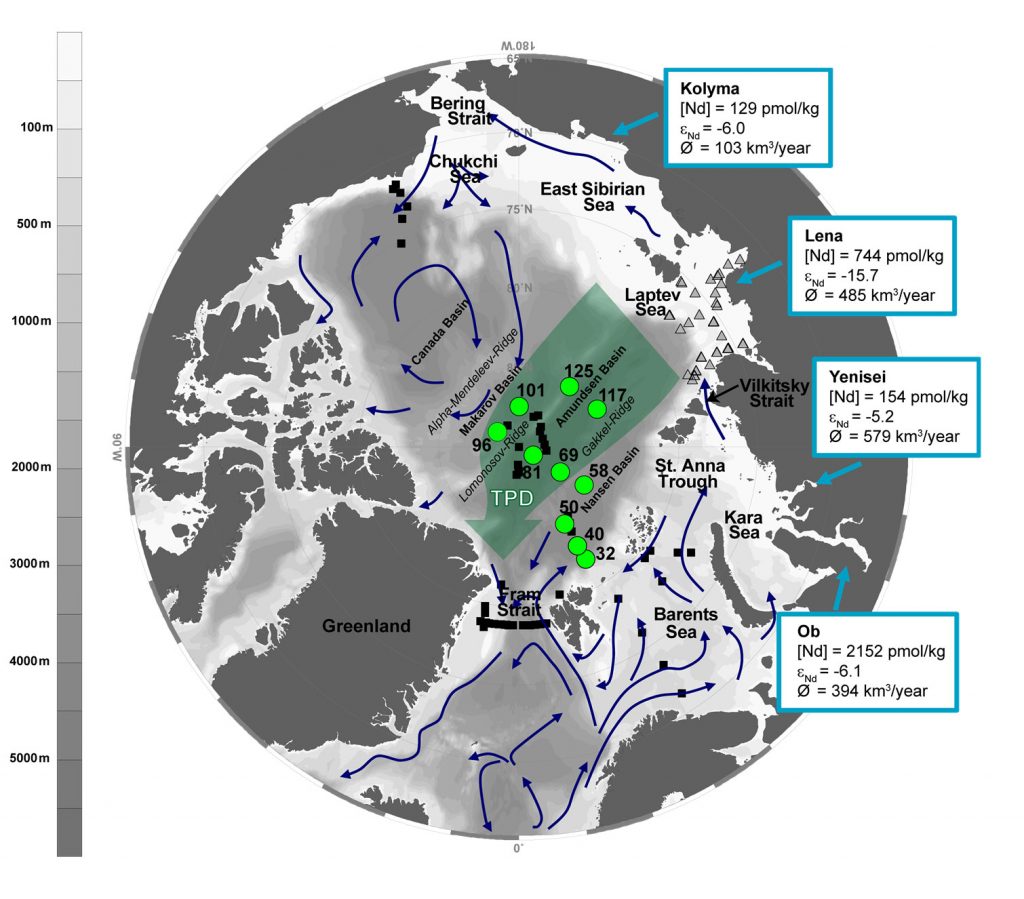
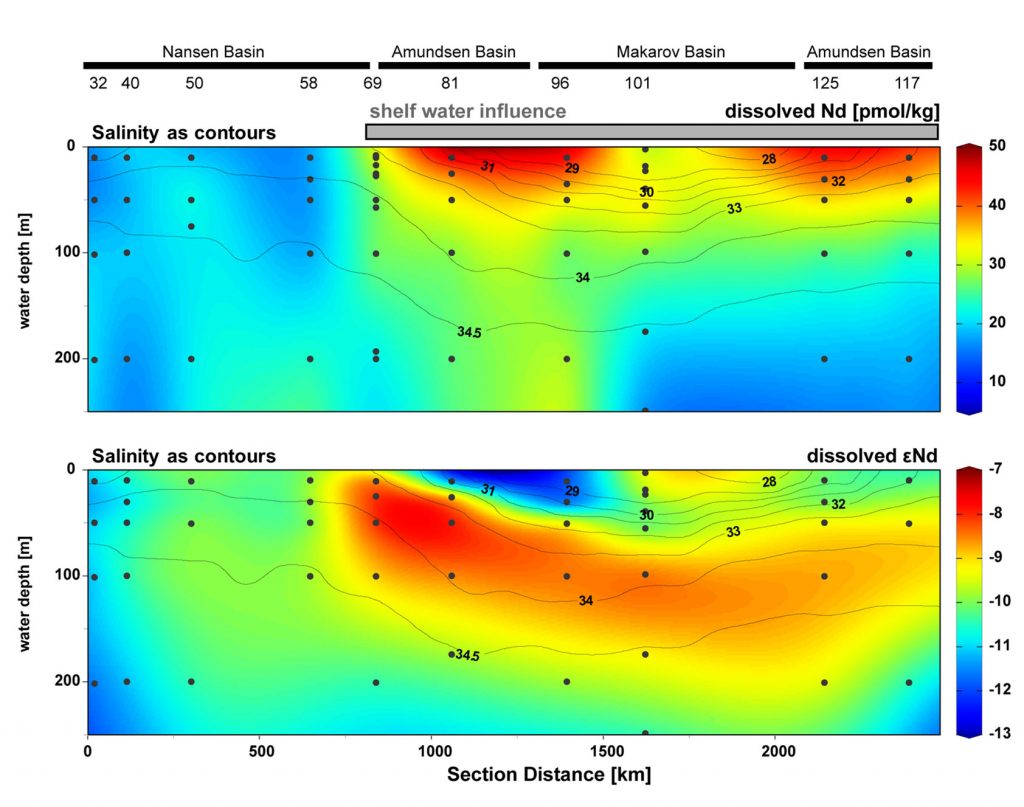
Figure: Map of the study region (left) and transects of Nd concentrations and Nd isotope compositions (εNd) in color (right). Station locations along the GEOTRACES GN04 cruise transect in the central Arctic Ocean as light green dots. Black squares and grey triangles mark the locations of other stations sampled for REEs. Light blue arrows mark the areas of river input, the boxes provide river water Nd concentrations, εNd composition and average annual river discharge. Blue arrows show the schematic circulation of surface water. TPD: Transpolar Drift.
Within the TPD, high dissolved Nd concentrations reflect river input. A wide range of dissolved εNd in the TPD mark contributions from the Siberian rivers with their different characteristic εNd signatures. Using the εNd signatures the different river signals can still be distinguished far along the flow path of the TPD.
Reference:
Paffrath, R., Laukert, G., Bauch, D., Rutgers van der Loeff, M., & Pahnke, K. (2021). Separating individual contributions of major Siberian rivers in the Transpolar Drift of the Arctic Ocean. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 8216. Access the paper: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86948
