High production of methylmercury in the anoxic waters of the Black Sea
As part of the GEOTRACES MedBlack cruise, the research vessel Pelagia occupied 12 full-depth stations in the Black Sea along an East-West transect between July 13th and 25th, 2013. In the permanently anoxic waters of the Black Sea, a high fraction (up to 57%) of total mercury (HgT) was found to be methylmercury (MeHg). These levels are comparable to oxic open-ocean subsurface maxima. Using a 1D numerical model, the authors demonstrated that MeHg inputs from rivers, the Mediterranean Sea and sediments are negligible and that MeHg is produced in situ in the anoxic waters. The authors also reported an increasing trend of HgT and MeHg concentrations in the anoxic waters. The numerical modeling suggests that more drastic reductions of Hg emissions are required to reach decreasing Hg and MeHg levels in the Black Sea.
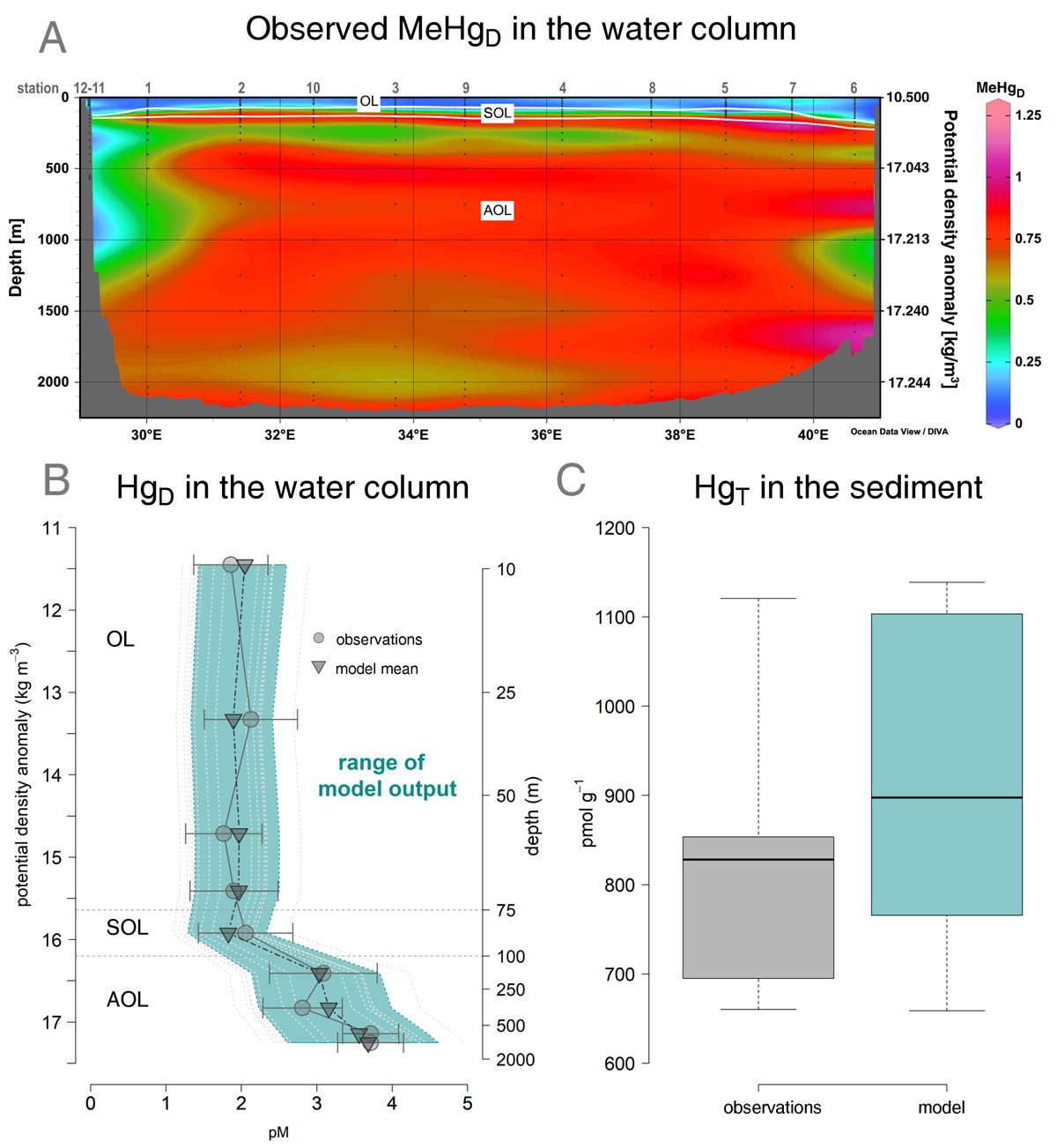 Figure: Concentrations of Hg species in the water column (OL = oxic layer, SOL = suboxic layer, AOL = anoxic layer) and sediments of the Black Sea. a) observed methylmercury (MeHg) distribution across the sampling stations of the GEOTRACES cruise; b) profile of dissolved Hg (HgD) observed (circles = layer means, bars = standard deviations) and modeled (triangles = model mean, coloured area = range of modeled concentrations) in the water; c) concentrations of total Hg (HgT) observed and modeled in the sediments. Click here to view the figure larger.
Figure: Concentrations of Hg species in the water column (OL = oxic layer, SOL = suboxic layer, AOL = anoxic layer) and sediments of the Black Sea. a) observed methylmercury (MeHg) distribution across the sampling stations of the GEOTRACES cruise; b) profile of dissolved Hg (HgD) observed (circles = layer means, bars = standard deviations) and modeled (triangles = model mean, coloured area = range of modeled concentrations) in the water; c) concentrations of total Hg (HgT) observed and modeled in the sediments. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Rosati, G., Heimbürger, L. E., Melaku Canu, D., Lagane, C., Laffont, L., Rijkenberg, M. J. A., Gerringa, L. J. A., Solidoro, C., Gencarelli, C. N., Hedgecock, I. M., De Baar, H. J. W., Sonke, J. E. (2018). Mercury in the Black Sea: new insights from measurements and numerical modeling. Global Biogeochemical Cycles. http://doi.org/10.1002/2017GB005700
