Mercury stable isotopes constrain atmospheric pathways to the ocean
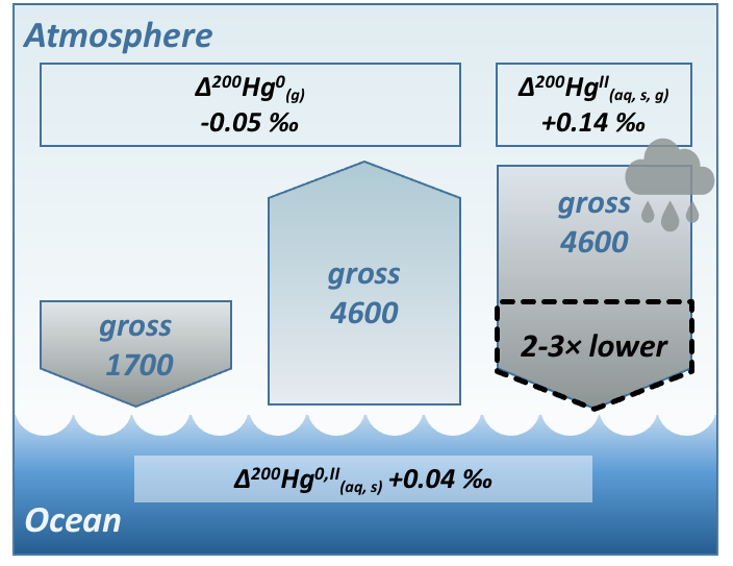
Mercury is one of the least concentrated trace elements in the ocean. Yet, the small seawater Hg levels biomagnify million times along the marine food chain, to reach harmful levels in predatory fish and their human consumers. Natural and anthropogenic Hg sources to the ocean remain ill-constrained. It took 10 years of development to come up with a method to measure Hg stable isotopes of seawater at subpicomolar levels. The Hg isotopic signatures in the ocean suggest the gas uptake (Hg0) and ionic deposition (HgII) are equally important (1:1), which is contrary than our current understanding (1:3)[1]. HgII deposition is likely overestimated by 2 to 3-fold, and the ocean receives less Hg overall. The study’s results hold promise that the implementation of anti-pollution measures under the Minamata Convention[2] will likely result in a faster decrease of oceanic Hg levels than previously thought.
Reference:
Jiskra, M., Heimbürger-Boavida, L., Desgranges, M., Petrova, M., Dufour, A., Ferreira-Araujo, B., Masbou, J., Chmeleff, J., Thyssen, M., Point, D., Sonke, J. E. Mercury stable isotopes constrain atmospheric sources to the ocean. Nature, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03859-8
[1] https://www.unep.org/resources/publication/global-mercury-assessment-2018
