Important external dissolved iron inputs, HNLC water formation and strong biological seasonality explained in the North Pacific Ocean
Subarctic Pacific is known as High Nutrient, Low Chlorophyll (HNLC) area, where phytoplankton growth is limited by dissolved iron (DFe) availability. The biological activity in the surface waters is also characterized by a marked seasonality. Nishioka and Obata (2017, see reference below) propose a detailed DFe zonal section across the North Pacific (~47°N), realized in the framework of Japan-GEOTRACES programme. Their data reveal important external Fe sources at mid-depth from the Sea of Okhotsk, and the continental margin followed by long range transport in the formation of Fe-rich intermediate water, although these enriched waters do not reach the Alaskan Gyre. This work also enlights why surface macronutrient consumption differ between the western and eastern gyre. Both HNLC water formation in the subarctic Pacific and high amplitude of seasonal variation in biogeochemical parameters in the western subarctic gyre are explained.
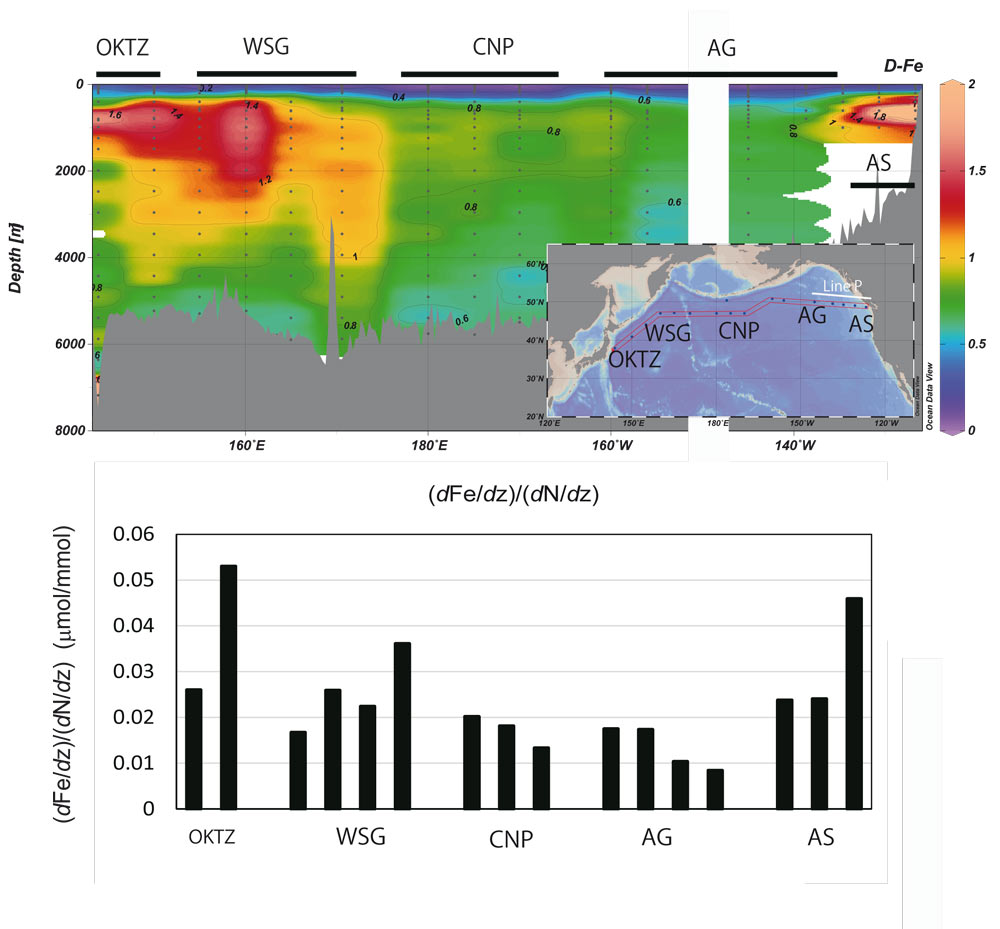
Figure: Dissolved Fe-rich intermediate water is transported laterally and distributed across the western subarctic gyre, over 2000 km (upper panel). The spatial pattern of Fe to nutrient stoichiometry supplied from the intermediate water to the surface (lower panel). Line P data is cited by Martin et al. 1989 and Nishioka et al. 2001. (OKTZ: Oyasio-Kuroshio transition zone, WSG: western subarctic gyre, CNP: central North Pacific, AG: Alaskan Gyre, AS: Alaskan stream). Click here to view the figure larger.
References:
Nishioka, J. and H. Obata, 2017, Dissolved iron distribution in the western and central subarctic Pacific: HNLC water formation and biogeochemical processes, Limnology and Oceanography, doi: 10.1002/lno.10548
Nishioka, J., S. Takeda, C. S. Wong, and W. K. Johnson. 2001. Size-fractionated iron concentrations in the northeast Pacific Ocean: distribution of soluble and small colloidal iron. Mar. Chem. 74: 157-179. doi:10.1016/S0304-4203(01)00013-5
Martin, J. H., R. M. Gordon, S. Fitzwater, and W.W. Broenkow. 1989. VERTEX: Phytoplankton/iron studies in the Gulf of Alaska. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 36(5): 649–680. doi:10.1016/0198-0149(89)90144-1
