Internal tides, energetic dynamical processes that generate particle nepheloids at different depths
Along the GEOVIDE (GA01) section, Lagarde and co-authors (2020, see reference below) evidenced clouds of lithogenic particles at various depths, from the Iberian continental slope to thousands of kilometers away (Read prior science highlight about it). Internal tides are waves with a tidal period generated when tides cross a steep slope of the sea floor. The encounter of internal tides with underwater relief results in high bottom friction that enhances sediment resuspension. In this study, Barbot and co-authors (2022, see reference below) identified the sites where internal tides are responsible for sediment resuspension along the same margin and section (figure A). The coupling of the internal tide energy dissipation model with a circulation one allows them to establish the trajectories of the resuspended sediment that explain the clouds of lithogenic particles measured along the GEOVIDE section (figure C).
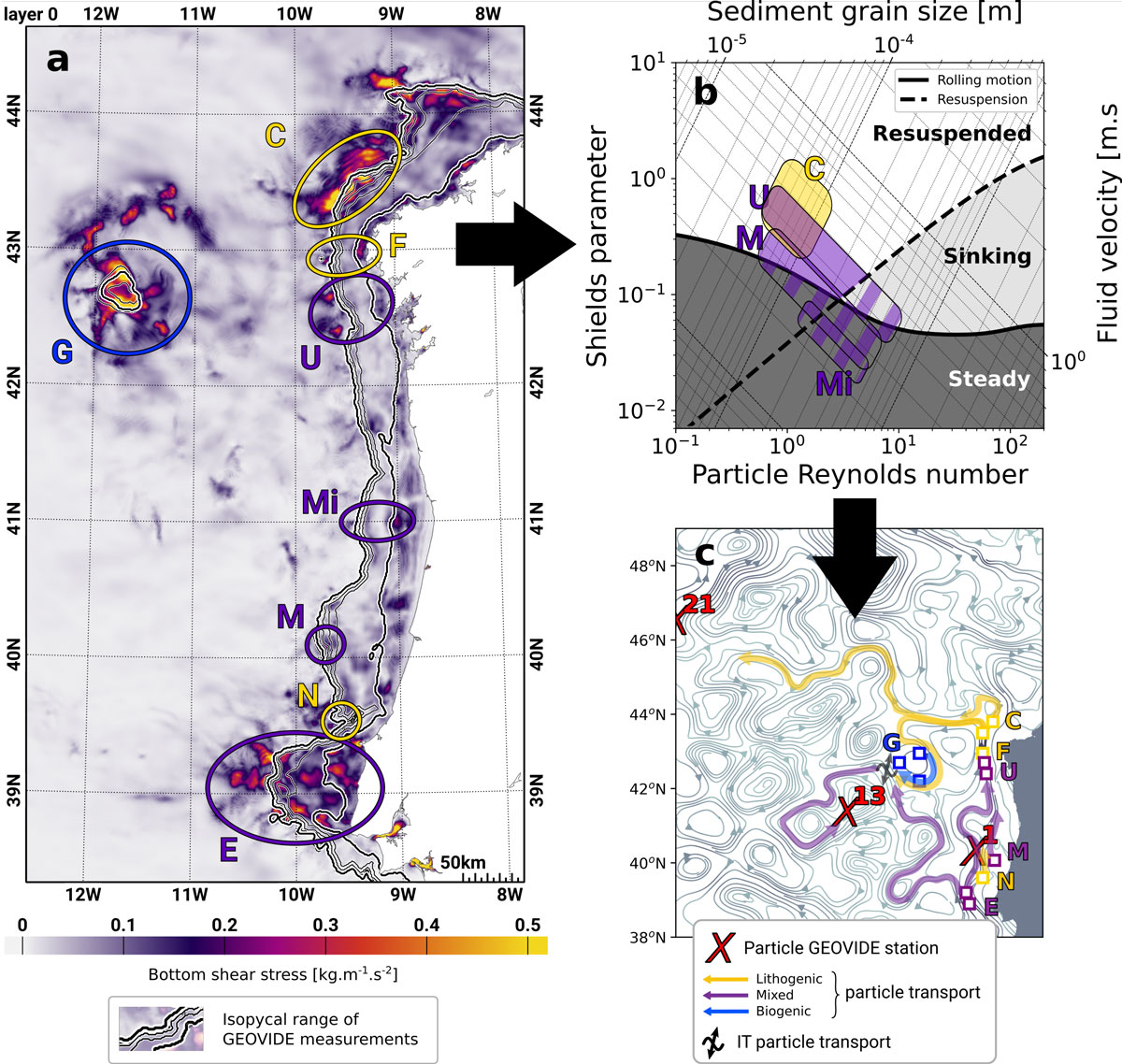
(b) For these identified sites, authors determined if sediment properties allow sediment resuspension. The graph shows the sediment properties for some of the sites. It confirms that most of the sediments are resuspended (above the black and dotted lines means the particles remain in suspension).
(c) Then, for resuspended particles, authors established the potential trajectories through general circulation, explaining the GEOVIDE cruise measurements (red crosses). The arrow colour corresponds to the nature of the sediment (yellow for lithogenic, blue for biogenic and purple for a mixture of both).
References:
Barbot, S., Lagarde, M., Lyard, F., Marsaleix, P., Lherminier, P., & Jeandel, C. (2022). Internal Tides Responsible for Lithogenic Inputs Along the Iberian Continental Slope. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 127(10). Access the paper: https://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2022jc018816
Lagarde, M., Lemaitre, N., Planquette, H., Grenier, M., Belhadj, M., Lherminier, P., & Jeandel, C. (2020). Particulate rare earth element behavior in the North Atlantic (GEOVIDE cruise). Biogeosciences, 17(22), 5539–5561. Access the paper: https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-17-5539-2020
