In situ detection of Particulate Inorganic Carbon using optical sensors
Jim Bishop and his colleagues (2022, see reference below) have developed optical sensors for particulate inorganic carbon (PIC) concentration that exploit the high mineral birefringence of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals. This innovative system allows collecting real-time particle concentration and composition data when deployed operationally from ship CTDs and ARGO-style Carbon Flux Explorer floats. Complementary to remote sensing, it provides PIC concentration vertical profiles, quite variable but essential data to constrain the suspended particle flux. When birefringent enough, clay occurrence in the particle pool can also be detected. The sensors were validated by comparing their data with i) CTD-Bottle suspension profiles, ii) particle data collected with large volume filtration systems (in situ pumps) and iii) eventually, at the surface, remote sensing retrievals of PIC.
In the end, the sensor only responds to the birefringent components of the total material in suspension. The PIC concentration sensor can detect PIC concentration variability from 0.01 to>1 μM in the water column: a development full of promises!
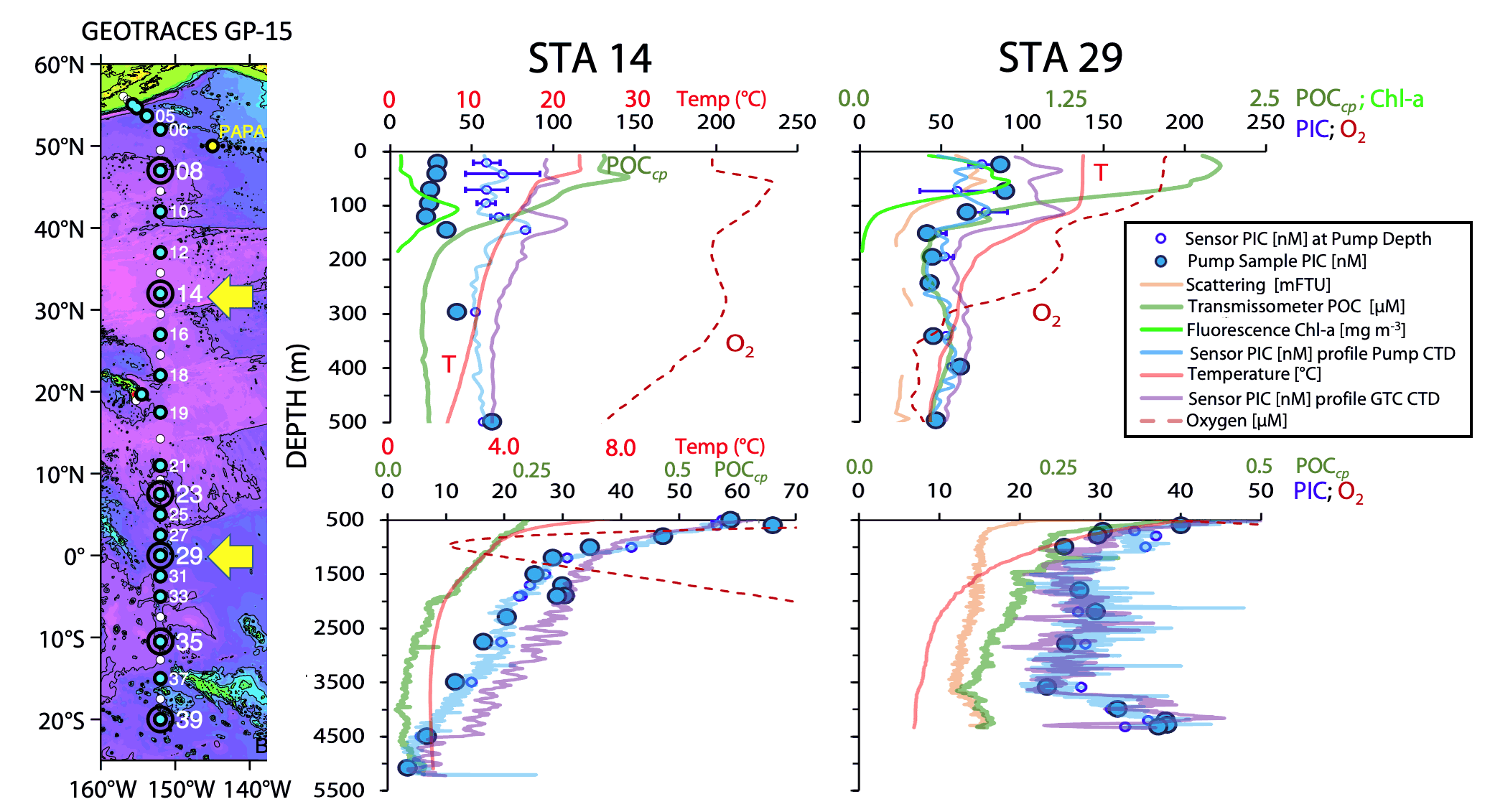
Figure: Map showing locations and bathymetric context for the surface to bottom profiling of two novel laser polarization sensors designed to detect concentrations of particulate inorganic carbon (PIC) during the 2018 GEOTRACES GP15 transect. Yellow arrows indicate locations of stations 14 and 23 where profile data are shown to the right side of the map. Blue and purple line depict PIC profiles from the two sensors. Large blue circles denote laboratory measured PIC concentrations from in-situ pump samples; small blue symbols denote sensor PIC at the same depth and time as sample collection. Also shown are chlorophyll fluorescence (bright green), scattering (light brown), particulate organic carbon (POC) calculated from beam attenuation coefficient. Redrawn from Figure 10c of Bishop et al. (2022).
Reference:
Bishop, J. K. B., Amaral, V. J., Lam, P. J., Wood, T. J., Lee, J.-M., Laubach, A., Barnard, A., Derr, A., & Orrico, C. (2022). Transmitted Cross-Polarized Light Detection of Particulate Inorganic Carbon Concentrations and Fluxes in the Ocean Water Column: Ships to ARGO Floats. Frontiers in Remote Sensing, 3. doi:10.3389/frsen.2022.837938
