Icebergs as sources of trace metals to the ocean: which impact?
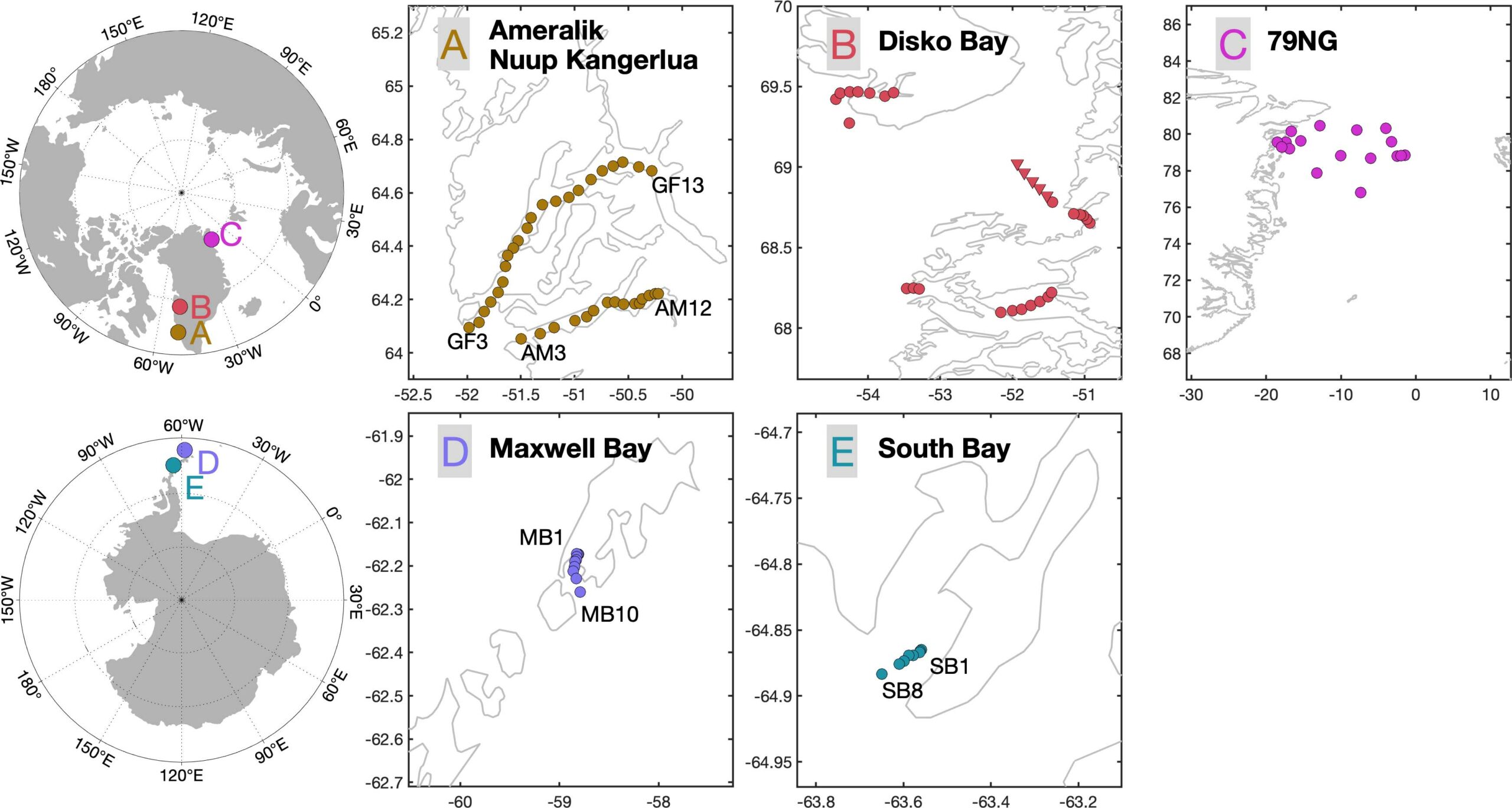
Earth’s Ice Sheets are known to release significant quantities of lithogenic particles into the ocean every year, but how does this material affect trace metal availability in the ocean? Combining results from GEOTRACES cruise GN05 at the ‘79° N Glacier’ with inshore work in Greenland and the Western Antarctic Peninsula, Krause et colleagues (2021, see reference below), present trends in dissolved iron, cobalt, nickel and copper across the glacier-to-ocean salinity gradient. Elevated signals of all metals are associated with glacier runoff, although ~98% of dissolved iron supplied from freshwater is rapidly returned to particulate phases. Curiously, dissolved iron concentrations in particular appeared to be strongly buffered in inshore waters throughout spring and summer, which means lateral fluxes from fjord over-turning may be a key driver of lateral trace element export year-round.
Reference:
Krause, J., Hopwood, M. J., Höfer, J., Krisch, S., Achterberg, E. P., Alarcón, E., Carroll, D., González, H. E., Juul-Pedersen, T., Liu, T., Lodeiro, P., Meire, L., Rosing, M. T. (2021). Trace Element (Fe, Co, Ni and Cu) Dynamics Across the Salinity Gradient in Arctic and Antarctic Glacier Fjords. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9, 878. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.725279
