What controls hydrothermal plume transport of iron over 4000 km in the deep Pacific Ocean?
The striking extension of the dissolved iron and manganese plumes over more than 4000 km from their hydrothermal sources along the US GEOTRACES East Pacific Zonal Transect (EPZT) cruise (GP16) has challenged our understanding of these element cycles (Resing et al., 2015 see GEOTRACES science highlight).
Fitzsimmons and co-workers (2017, see reference below) analysed the particulate iron and manganese (Mn) in the same plume and showed that they also exceed background concentrations, even 4,000 km from the vent source, despite anticipated gravitational settling losses. Both dissolved and particulate Fe plumes deepen by more than 350 m relative to the conservative helium-3 (3He) one, while the Mn plumes do not show such descent.
Based on Fe speciation and isotope data, the authors suggest that dissolved iron fluxes and geospatial positioning may depend on the balance between stabilization in the dissolved phase by organic ligands and the reversibility of exchange onto sinking particles.
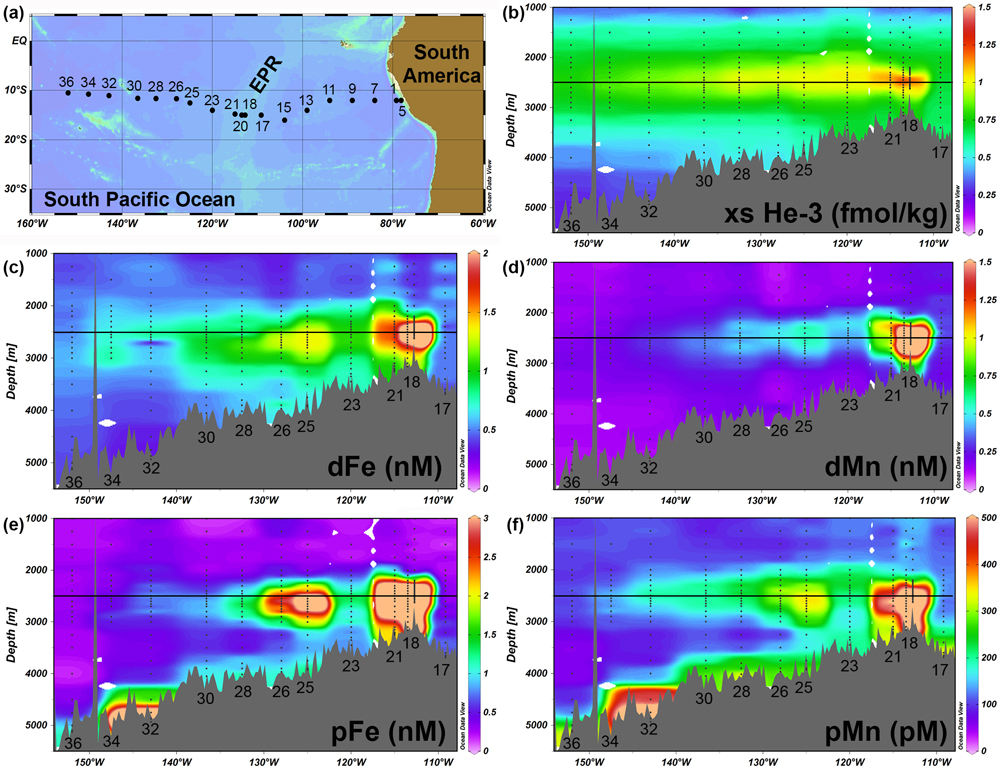
Figure: Interpolated concentrations and station map along the US GEOTRACES EPZT (GP16) section. a, Map of the station locations (colours corresponds to bathymetry; green hues shallower) b, Excess 3He concentrations in fmol kg−1. c, Dissolved Fe concentrations (<0.2 µm, in nM). d, Dissolved Mn concentrations (<0.2 µm, in nM). e, Particulate Fe (>0.45µm, in nM). f, Particulate Mn (>0.45µm, in pM). The black reference line at 2,500m in each panel highlights the deepening of the Fe plumes. Ocean Data View was used to carry out the simulations. Click here to view the figure larger.
References:
Fitzsimmons, J. N., John, S. G., Marsay, C. M., Hoffman, C. L., Nicholas, S. L., Toner, B. M., German, C. R., Sherrell, R. M. (2017). Iron persistence in a distal hydrothermal plume supported by dissolved-particulate exchange. Nature Geoscience. DOI: 10.1038/ngeo2900
Resing, J. A., Sedwick, P. N., German, C. R., Jenkins, W. J., Moffett, J. W., Sohst, B. M., & Tagliabue, A. (2015). Basin-scale transport of hydrothermal dissolved metals across the South Pacific Ocean. Nature, 523(7559), 200–203. DOI: 10.1038/nature14577
