How iron isotopes offer a new window on the oceanic biogeochemical cycling of iron
Two process studies (2008 and 2012) designed to study temporal changes in the biogeochemical cycling of iron (Fe), provide in situ results for dissolved and particulate Fe (DFe and PFe) cycling during the annual spring bloom.
These field data have been complemented by a shipboard 700-L mesocosm incubation experiment. Later, a conceptual model helps figuring out the key chemical and biological processes involved in Fe isotope fractionation.
This works demonstrates that DFe is isotopically lighter than PFe at the beginning of the spring, likely reflecting the reduction of PFe by photochemistry and bacteria-mediated reduction processes. As the bloom develops, DFe within the surface mixed layer becomes isotopically heavier, consistent with the preferential uptake of light iron by phytoplankton while scavenging appears to play a minor role in fractionating Fe.
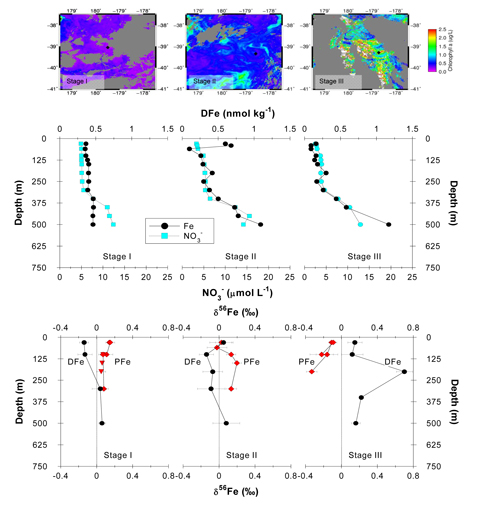
Figure. This figure shows the increase in chlorophyll concentration across three different stages of the subtropical phytoplankton bloom (upper panels), along with depth profiles for dissolved iron and nitrate (middle panels), and the iron isotope composition of dissolved and particule iron (lower panels). Disssolved iron (DFe) is isotopically lighter (negative values) than particulate iron (PFe) at the beginning of the spring (stage I). As the bloom develops, DFe within the surface mixed layer becomes isotopically heavier (more positive values), consistent with the preferential uptake of light iron by phytoplankton. Click here to view the image larger.
Reference:
Ellwood, M. J., Hutchins, D. A., Lohan, M. C., Milne, A., Nasemann, P., Nodder, S. D., Sander, S.G., Strzepek, R., Wilhelm, S.W., Boyd, P. W. (2014). Iron stable isotopes track pelagic iron cycling during a subtropical phytoplankton bloom. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(1), E15–20. doi:10.1073/pnas.1421576112. Click here to access the paper.
