Deep-sea mining, dewatering waste, accidental plumes and their potential consequences on trace metal fates in the North Pacific Ocean
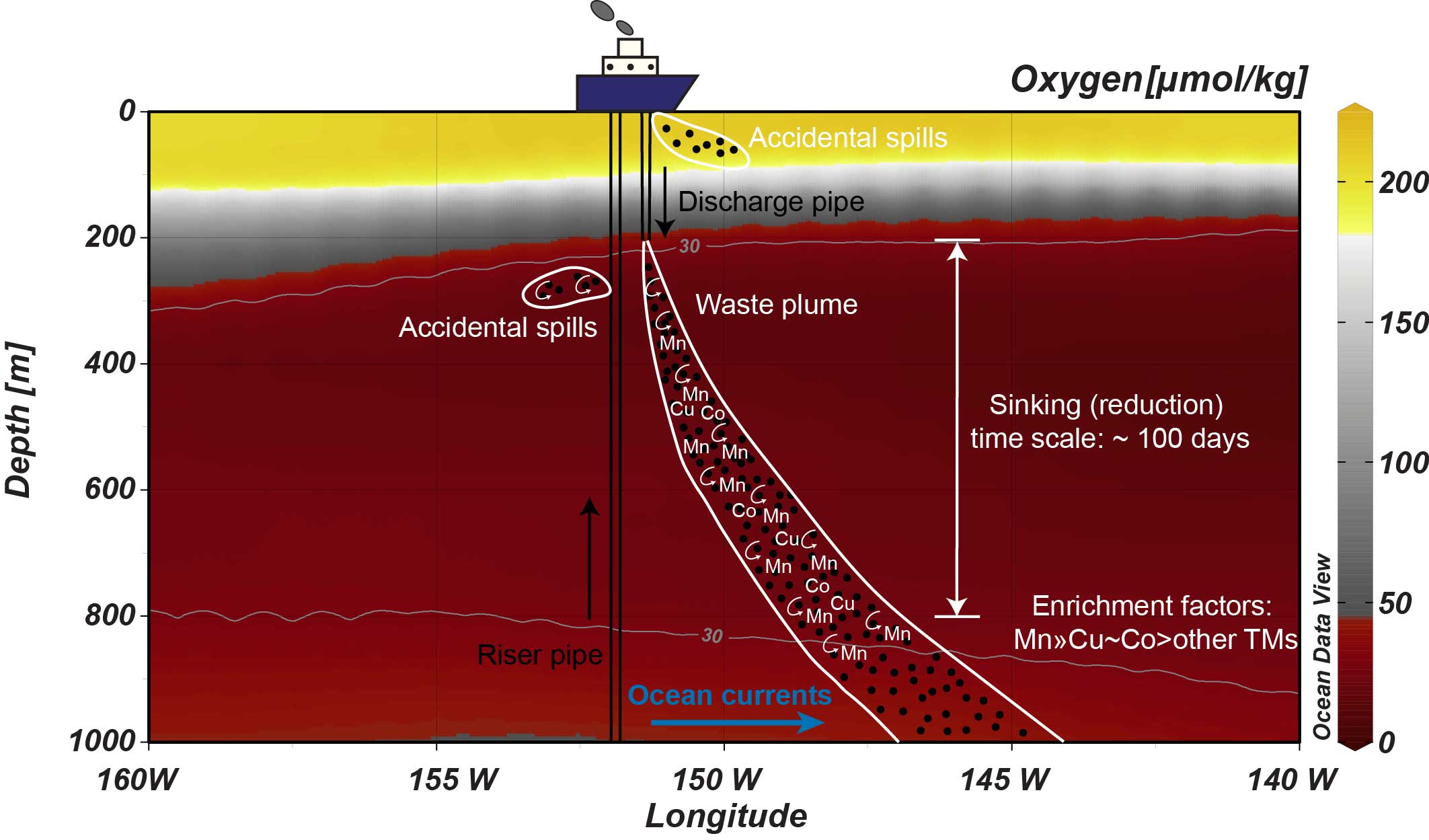
While attention to potential future deep sea mining projects intensifies, very few studies estimated the geochemical and environmental consequences of mining dewatering waste plume and accidental spills from both the riser pipe and the mining platform into the abyssal waters. Xiang and his colleagues (2024, see reference below) conducted laboratory incubation experiments that simulate mining discharge into anoxic waters. The choice of using anoxic waters during the incubation is driven by the fact that oxygen depleted waters (ODZ) are overlying potential mining sites in the North Pacific Ocean. During the ∼100 days for crushed manganese (Mn) nodules to sink through the 600 m-thick ODZ, their results show that cobalt (Co) or copper (Cu) -together with Mn – could be the most enriched trace metal within the waste plume compared to the background seawater concentration. The possible enrichment of dissolved Cu in the waste plume may be a concern given its strong toxicity to some phytoplankton. Its impact on the mesopelagic ecosystem needs to be better evaluated.
This paper made the cover of the ACS ES&T Water magazine (see figure below). Congratulations to the authors!
References:
Xiang, Y., Steffen, J. M., Lam, P. J., Gartman, A., Mizell, K., & Fitzsimmons, J. N. (2024). Metal Release from Manganese Nodules in Anoxic Seawater and Implications for Deep-Sea Mining Dewatering Operations. ACS ES&T Water, 4, 2957–2967. Access the paper: 10.1021/acsestwater.4c00166
Boyer, T. P.; García, H. E.; Locarnini, R. A.; Zweng, M. M.; Mishonov, A. V.; Reagan, J. R.; Weathers, K. A.; Baranova, O. K.; Paver, C. R.; Seidov, D.; Smolyar, I. V., World Ocean Atlas 2018. Oxygen. In NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, 2018.
