Gulf stream eddies are fertilizing the Western Atlantic Ocean
Tim Conway and co-authors (2018, see reference below) show that Gulf Steam eddies can provide an extra supply of iron, and nutrients such as phosphate and nitrate to the iron-starved Western Atlantic Ocean. Gulf stream eddies form when the northward fast-flowing Gulf Stream meanders and pinches off coastal water, spinning these ‘rings’ out into the ocean. This coastal water is rich in iron. The authors used satellite and ocean datasets to show that these eddies may be just as important than dust in supplying iron to this area of the ocean!
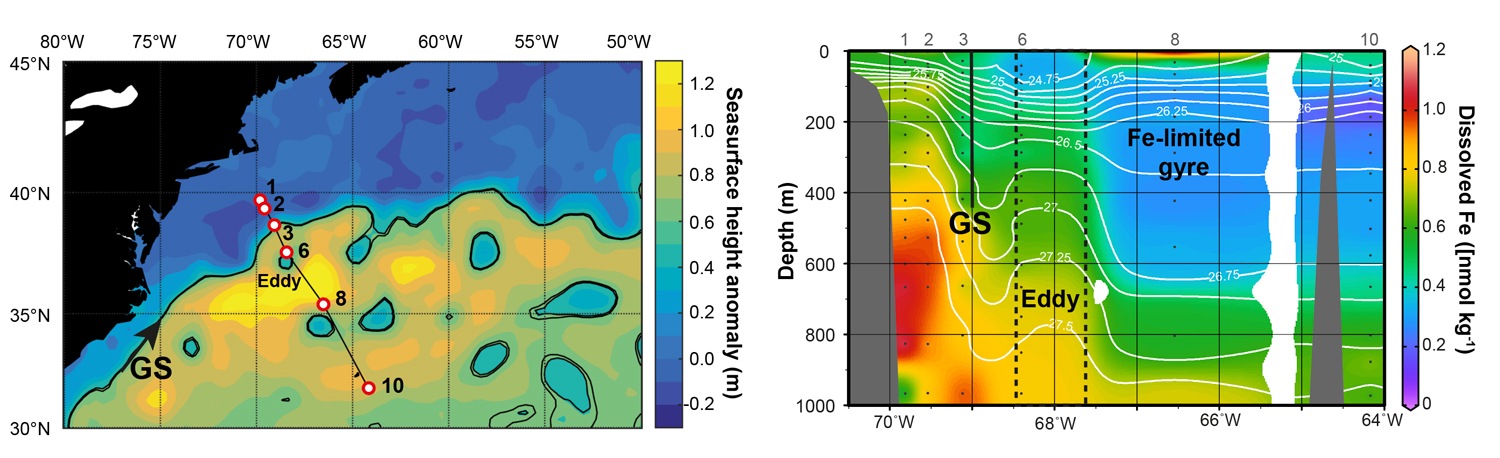 Figure: Cruise track (left) and dissolved iron (Fe) concentrations (right) from a North Atlantic GEOTRACES dataset (GA03). The northward flowing Gulf Stream (labelled GS) can be clearly picked out as the boundary between the coastal Slope Water which is enriched in Fe, and the open gyre which is Fe-depleted. A gulf steam eddy (labelled) was serendipitously sampled on the cruise, and can be seen as carrying a column of water enriched in Fe across the Gulf Stream and out into the gyre. The authors used this chemical dataset, together with satellite data to calculate how much iron eddies carry into the gyre each year. Click here to view the image larger.
Figure: Cruise track (left) and dissolved iron (Fe) concentrations (right) from a North Atlantic GEOTRACES dataset (GA03). The northward flowing Gulf Stream (labelled GS) can be clearly picked out as the boundary between the coastal Slope Water which is enriched in Fe, and the open gyre which is Fe-depleted. A gulf steam eddy (labelled) was serendipitously sampled on the cruise, and can be seen as carrying a column of water enriched in Fe across the Gulf Stream and out into the gyre. The authors used this chemical dataset, together with satellite data to calculate how much iron eddies carry into the gyre each year. Click here to view the image larger.
Reference:
Conway, T. M., Palter, J. B., & de Souza, G. F. (2018). Gulf Stream rings as a source of iron to the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Nature Geoscience, 1. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-018-0162-0
