Glacial erosion processes suspected to enhance the lability of particulate iron, with a strong influence on the biological demand in the subantarctic waters
As part of the GEOTRACES process study HEOBI (GIpr05) van der Merwe and co-workers (2019, see reference below) conducted a thorough characterization of the labile and refractory iron phases of the particles discharged to the local seawater by the glacial erosion and rivers of Heard and Mc Donald islands (Southern Indian Ocean). They demonstrate that, together with their specific lithology, the fraction of labile iron is significantly larger for particles that experienced glacial weathering processes than for particles of submarine hydrothermal origin. Moreover, they estimate that this labile particulate iron supplied from Heard and to a lesser extent, McDonald Island, is likely the missing iron required meeting biological demand over the plateau, downstream of the islands where traditionally an intense seasonal bloom develops.
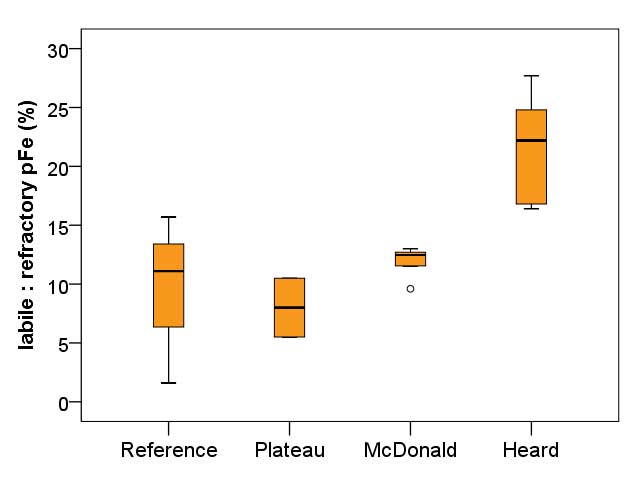
Figure: Mixed layer, mean labile fraction of pFe (ratio of labile to refractory pFe) at each of the contrasting regions within the study. Heard Island displayed a significantly higher mean labile fraction compared to all other sites, including the reference station (one-way ANOVA, Games-Howell post hoc, p < 0.01). Furthermore, in addition to the ratio of labile to refractory Fe being higher at Heard Island, the absolute concentration of labile particulate Fe (pFelab) was also significantly higher at Heard Island (115 ± 34 nM, n = 9) compared to McDonald Island (79 ± 20 nM, n = 12) (one-way ANOVA, Games-Howell post hoc, p < 0.01). Standard boxplot median (centre black line), 25th and 75th percentiles (upper and lower box limits) and 95% confidence intervals (inner fences) are indicated. Outliers are shown as open circles and defined as less than 1.5 times the interquartile range. The number of independent data points for the reference, plateau, McDonald and Heard regions were 3, 2, 8 and 9 respectively.
Reference:
van der Merwe, P., Wuttig, K., Holmes, T., Trull, T. W., Chase, Z., Townsend, A. T., Goemann, K., Bowie, A. R. (2019). High Lability Fe Particles Sourced From Glacial Erosion Can Meet Previously Unaccounted Biological Demand: Heard Island, Southern Ocean. Frontiers in Marine Science, 6, 332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00332
