Estuary solid loads and solid-solution exchanges yield considerable dissolved trace metal enrichments
Based on a thorough investigation of water and suspended sediment samples collected over two years and a six seasons, Samanta and Dalai (2018, see reference below) show that the annual dissolved fluxes of metals from the Ganga (Hooghly) River are enhanced by up to 230–1770% when compared to the conservative mixing. They clearly demonstrate that this enrichment results from exchange processes between the large solid load (suspended particles) and the waters of the middle and lower estuary. Groundwater and direct anthropogenic flux are negligible in these estuary segments.
On a broader scale, their work suggests that solute-particle interaction is a globally significant process in the estuarine production of dissolved metals. The authors estimate that although South Asian Rivers account for only ~ 9% of the global riverwater flux, their high sediment loads results in contributing a far higher proportion of the global supply of the dissolved metals from the rivers: 40 ± 2% of nickel (Ni) and 15 ± 1% of copper (Cu).
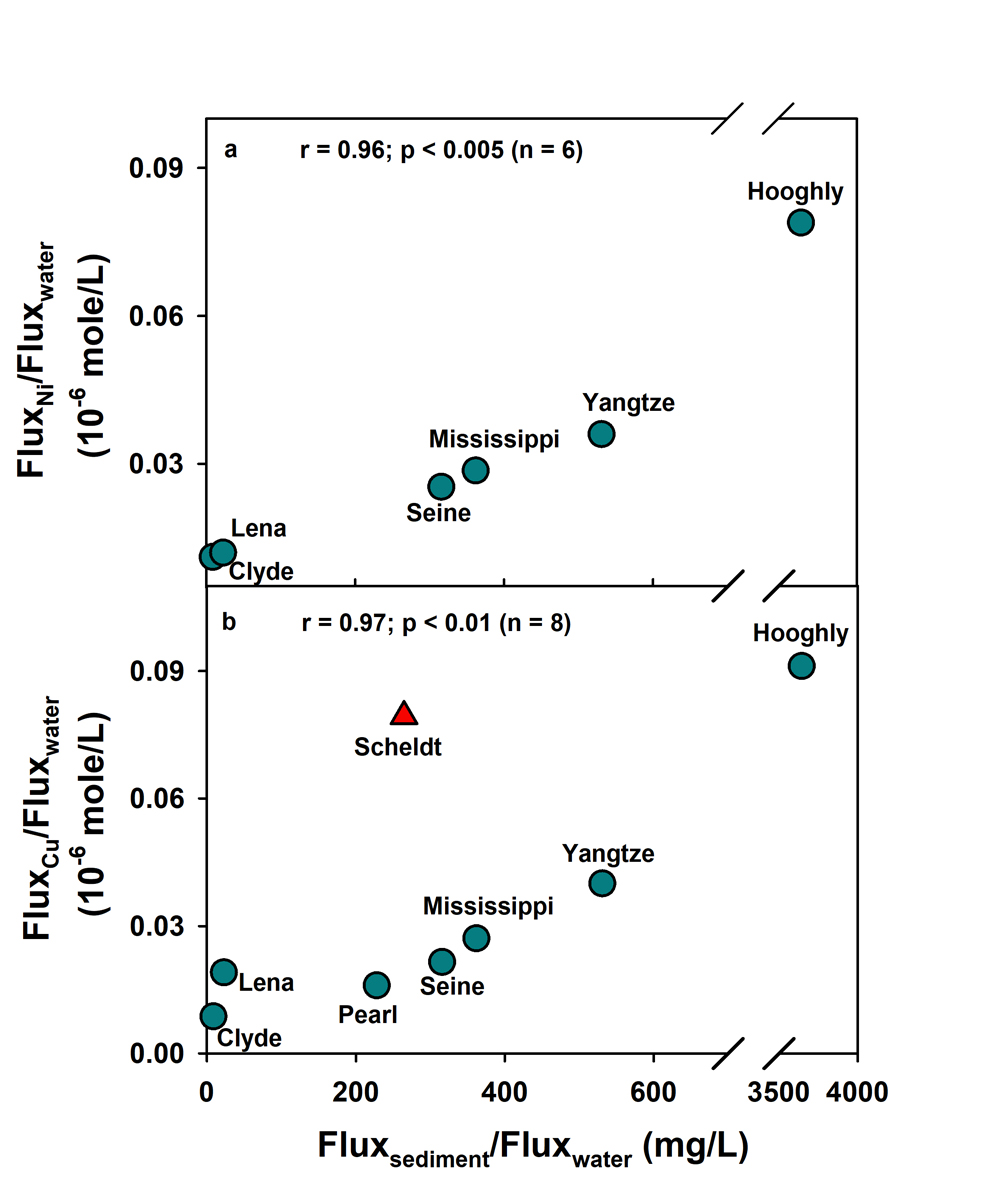 Figure: A plot of dissolved flux of nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu) vs. the sediment flux, after normalizing with the corresponding water flux, for the estuaries of some of the major rivers around the world where production of the metals is documented. The strong positive correlation is suggestive of the direct link between the solute-particle interaction and the estuarine production of the metals. The data of the river Scheldt is excluded from regression analysis. Click here to view the figure larger.
Figure: A plot of dissolved flux of nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu) vs. the sediment flux, after normalizing with the corresponding water flux, for the estuaries of some of the major rivers around the world where production of the metals is documented. The strong positive correlation is suggestive of the direct link between the solute-particle interaction and the estuarine production of the metals. The data of the river Scheldt is excluded from regression analysis. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Samanta, S., & Dalai, T. K. (2018). Massive production of heavymetals in the Ganga (Hooghly) River estuary, India: Global importance of solute-particle interaction and enhancedmetal fluxes to the oceans. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 228, 243–258. http://doi.org/10.1016/J.GCA.2018.03.002
