Dissolved manganese distribution in the Arabian Sea reveals many variable triggers
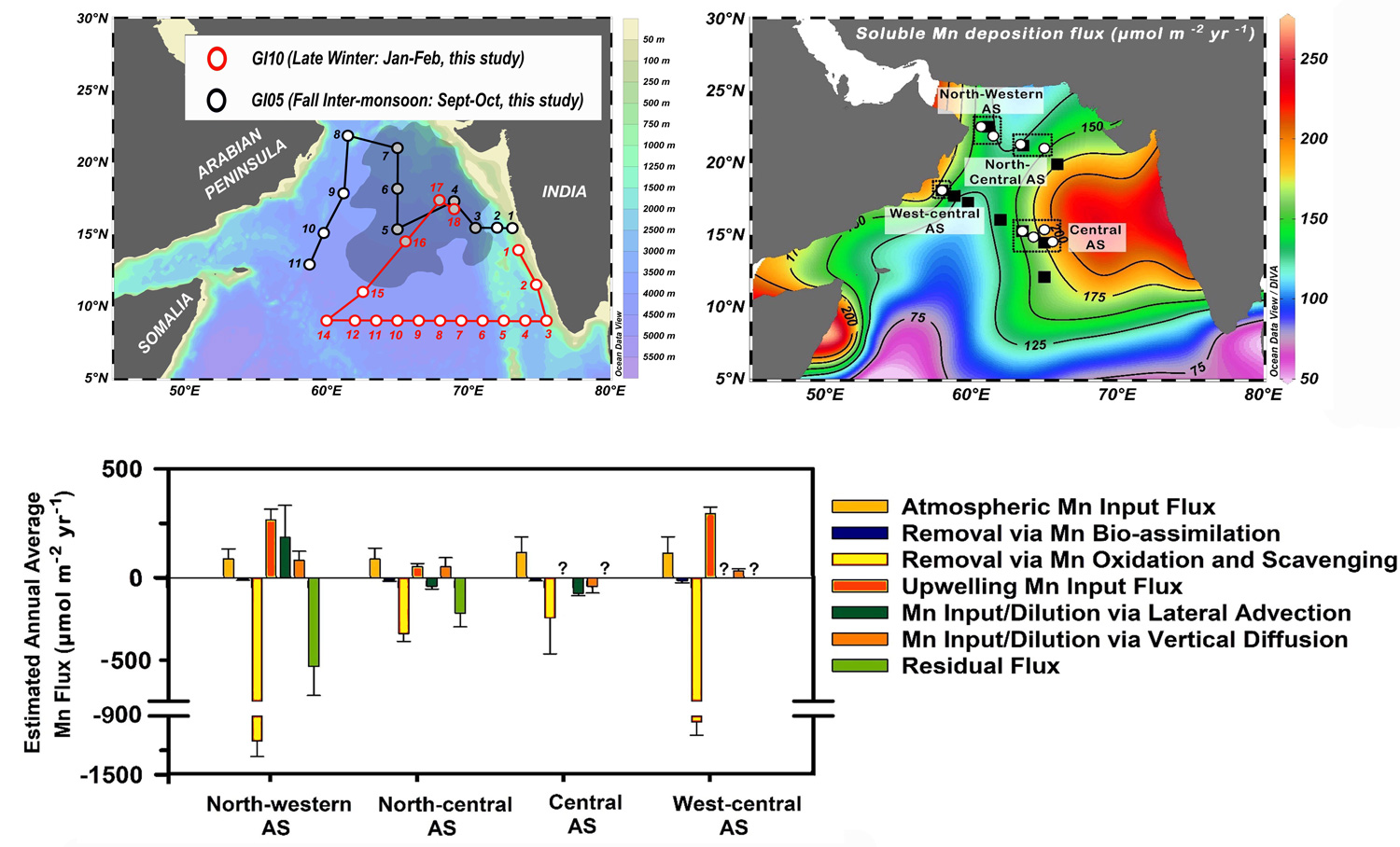
Analysis of dissolved manganese (dMn) on samples collected as part of the GEOTRACES cruises GI05 and GI10 allowed Singh and his colleagues (2023, see reference below) to establish the basin-wide distribution of this trace metal in the Arabian Sea. Interestingly, variable concentrations of dMn from surface to depth and from west to east reveal that the Arabian Sea is submitted to different forcings: surface atmospheric inputs induce a strong spatial gradient, with higher dMn concentration in the east (influence of wet atmospheric deposition and fluvial input) than in the west. Contrastingly, in the southern part of the basin, the data reveal the advection of dMn-rich, low-salinity Bay of Bengal surface waters. Below, observed dMn maxima reflects the strong change of environmental condition in the oxygen minimum zone: under the reduction of Mn oxides, dMn concentrations increase in the water column at depth around 200-400 m; in addition, at the same depth, the influence of lateral inputs from reducing sediments is also detected. The margin influence is also observed in the northern part of the section, from sediments of the Pakistan margin. While the dMn concentrations are low below 1500m, local enrichments are likely due to hydrothermal inputs on the one hand and sediment resuspension on the other hand.
Reference:
Singh, N. D., Singh, S. K., Malla, N., & Chinni, V. (2023). Biogeochemical cycling of dissolved manganese in the Arabian Sea. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 343, 396–415. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2022.12.030
