Dissolved gallium unravels Pacific and Atlantic waters in the Arctic Ocean
In the Arctic Ocean, the relative amounts of Pacific and North Atlantic-derived water affect its heat and salt balance which, in turn, affects climate-relevant processes such as the formation of of Arctic sea ice. Previous attempts to deconvolve these sources have utilized nutrient-based tracers which have been unsatisfying because the nutrients are non-conservative in ways that are difficult to compensate for.
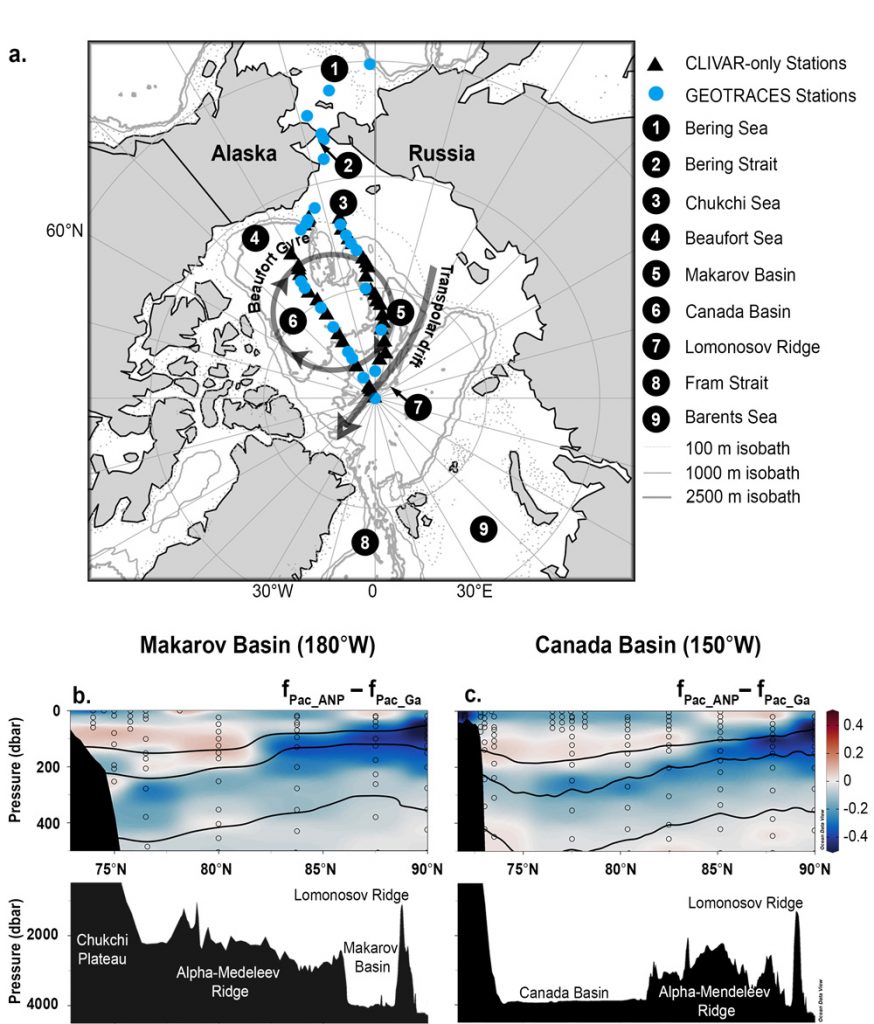
Whitmore and co-workers (2020, see reference below) demonstrate that the dissolved gallium (Ga) distribution is conservative enough in the Arctic to provide a better water source deconvolution than the nutrient tracers.
Indeed, dissolved Ga concentrations show measurable contrast between Atlantic and Pacific source waters, shelf‐influenced waters show little impact of shelf processes on the dissolved Ga distribution, and dissolved Ga in the Arctic basins is conserved along isopycnal surfaces. Among others, the authors reveal that use of Ga as tracer yields a more realistic vertical transition between Pacific and Atlantic waters than the nutrient method with the result that there appears to be more Pacific sourced water than previously estimated.
Reference:
Whitmore, L. M., Pasqualini, A., Newton, R., & Shiller, A. M. (2020). Gallium: A New Tracer of Pacific Water in the Arctic Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 125(7). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JC015842
