Debate on the dissolved nickel bioavailibility in surface waters
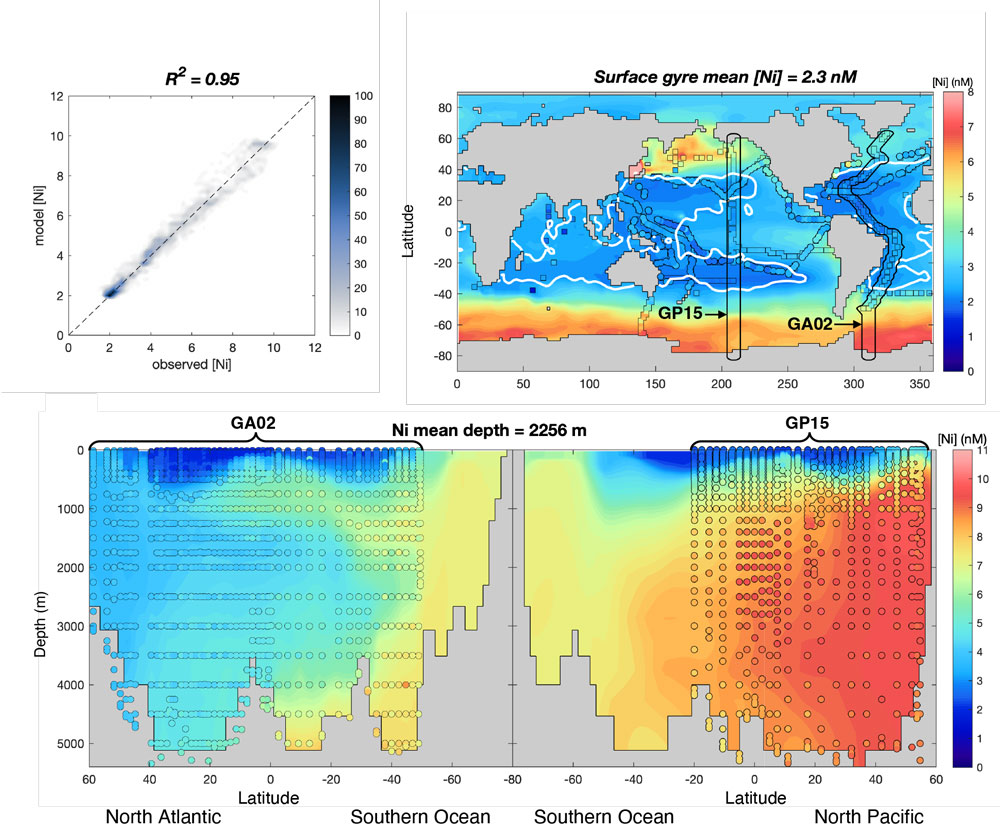
John and co-authors (2022, see reference below) tackle one of the known paradoxes regarding trace metal cycles in the ocean: the dissolved nickel (Ni) leftover systematically observed in surface waters while Ni is a limiting factor for the phytoplankton development. Their strategy follows a double approach: test of the lability and bioavailability of Ni in the surface ocean using trace metal extraction from surface waters using chelating resins and controlled phytoplankton cultures, respectively; test of what controls the fluxes of Ni into the deeper ocean, with regards to the phosphate export and remineralization. These two main processes that govern the Ni cycles are thus confronted to field and experimental data using 7 different sensitivity tests with the AWSOME-OCIM model. In the end, the authors suggest that slow depletion of Ni relative to macronutrients in upwelling regions can explain the residual Ni pool. They also propose that slower regeneration of Ni compared with macronutrients explains the strong Ni enrichment in deep waters.
Reference:
John, S. G., Kelly, R. L., Bian, X., Fu, F., Smith, M. I., Lanning, N. T., Liang, H., Pasquier, B., Seelen, E. A., Holzer, M., Wasylenki, L., Conway, T. M., Fitzsimmons, J. N., Hutchins, D. A., & Yang, S.-C. (2022). The biogeochemical balance of oceanic nickel cycling. Nature Geoscience. Access the paper:10.1038/s41561-022-01045-7
