Constraining Oceanic Copper Cycling through Artificial Intelligence and Ocean Circulation Inverse Model
Using available observations of dissolved copper (Cu), artificial neural networks, and an ocean circulation inverse model, Roshan and collaborators (2020, see references below) calculated a global estimate of the 3-dimensional distribution and cycling of dissolved Cu in the ocean (see Figure). Among the most striking features, they reveal that: (1) the highest surface dissolved Cu concentrations and the highest rates of dissolved Cu export occur in the Southern Ocean and, and (2) Cu is removed predominantly in the ocean interior but a near-sediment source sustains its vertical accumulation.
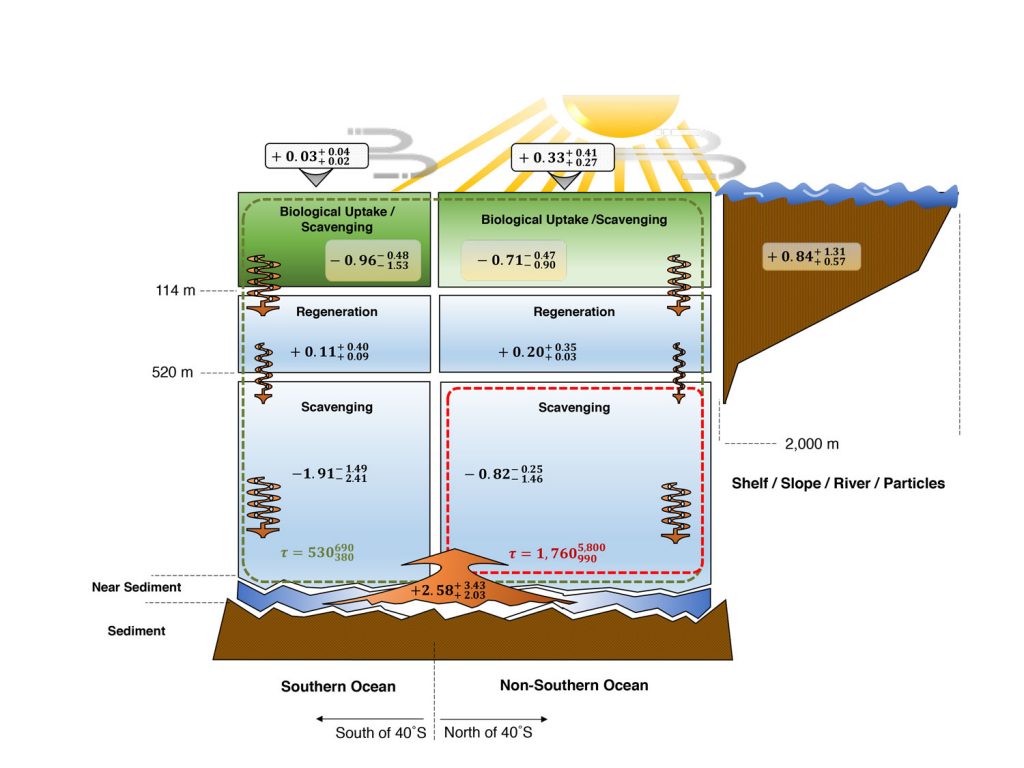
References:
Roshan, S., DeVries, T., & Wu, J. (2020). Constraining the Global Ocean Cu Cycle With a Data‐Assimilated Diagnostic Model. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GB006741
Roshan, S., DeVries, T. & Wu, J. (2020). Dissolved Copper Climatology. figshare. DOI: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.11827908.v2
