Influence of particle composition on the rate constants of thorium adsorption
Chemical species are constantly exchanged between seawater (solution, D) and particles (solid material, P). This continuous D-P exchange is a key process determining the chemical composition of the ocean. Particles are heterogeneous materials, made of (i) biological material from the surface ocean, (ii) lithogenic material from external inputs to the ocean, and (iii) authigenic (oxyhydr)oxides precipitation in the water column. Understanding the role of each of these phases in driving the D-P exchange is therefore a major issue.
Lerner and co-workers (2018, see reference below) propose to disentangle the particle composition effect on the thorium adsorption rate constant k1 using two different regression models. Model I considers biogenic particles, lithogenic particles, Mn (oxyhydr)oxides, and Fe (oxyhydr)oxides as regressors, and k1 as the regressand. Model II considers ln(biogenic particles), ln(lithogenic particles), ln(Mn (oxyhydr)oxides), and ln(Fe (oxyhydr)oxides) as regressors, and ln(k1) as the regressand, where ln() denotes the natural logarithm. Thus, models I and II posit that the effects of particle phases on k1 are, respectively, additive and multiplicative. Regressions are considered separately in two regions of the North Atlantic: an upwelling region off the western margin of Mauritania, and an open-ocean region east of Bermuda.
The authors find that model II better describes the effect of particle composition on k1. Based on this regression model, the authors find that Mn (oxyhydr)oxides have a stronger effect on k1 in the open-ocean region, and biogenic particles have a stronger effect on k1 in the upwelling region.
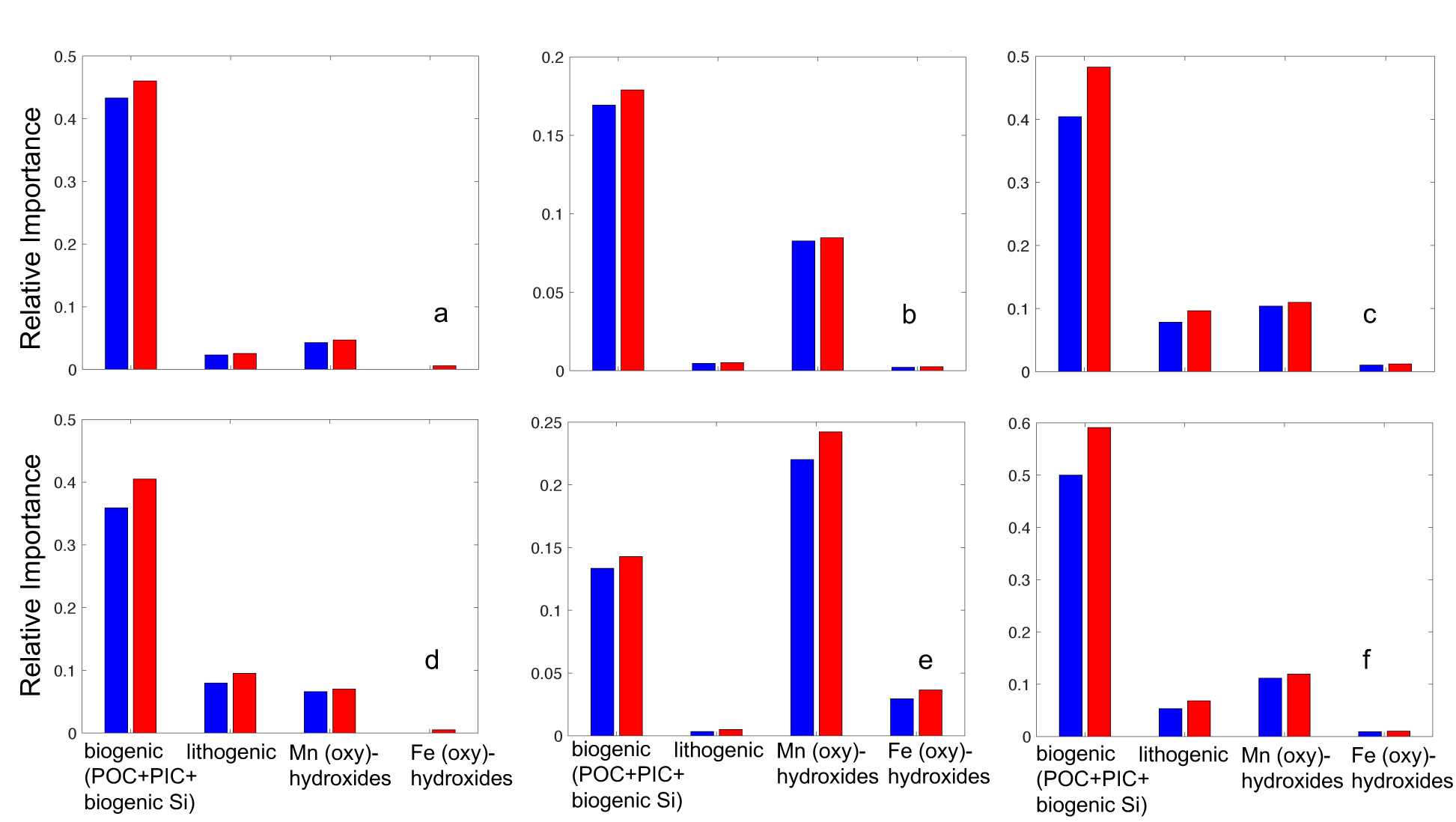
Figure: Relative Importance (RI) of particle phases for influencing the thorium adsorption rate constant, k1, under the additive model (upper panels) and the multiplicative model (lower panels). Results shown at all stations (a,d), open-ocean stations (b,e), and Mauritanian upwelling stations (c,f). The red and blue bars show two different methods to obtain RI values. Biogenic particles and Mn (oxyhydr)oxides have the strongest relationship to k1, depending on the model and stations considered. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Lerner, P., Marchal, O., Lam, P. J., & Solow, A. (2018). Effects of particle composition on thorium scavenging in the North Atlantic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 233, 115–134. http://doi.org/10.1016/J.GCA.2018.04.035
