Are the pelagic clay-rich sediments a major source of elements to bottom-waters?
Although pelagic red clay sediments (which represents almost 40% of the global ocean seafloor) are suspected to be a significant source of trace elements to the water column, very few data are available today to dimension this bottom source.
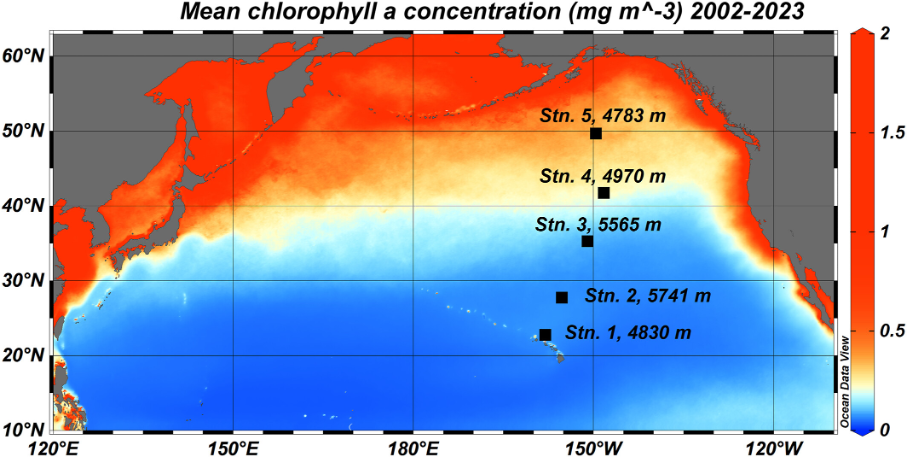
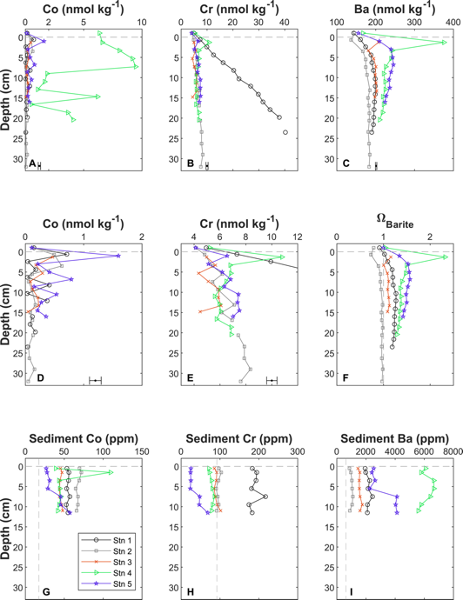
Steiner and colleagues (2023, see reference below) proposed to tackle this issue by analyzing porewater and bulk sediment concentrations of vanadium, chromium, cobalt, nickel, copper, arsenic, molybdenum, barium and uranium, as well as concentrations of the major oxidants nitrate, manganese, iron, and sulfate in the top 30 cm of 5 cores collected along a transect from Hawaii to Alaska. They establish that:
- Porewater transition metal concentrations vary by up to an order of magnitude in aerobic pelagic clay sediments. Large concentration variability is not always requiring significant changes in redox conditions, because they can be due to the nature and quantity of material falling on the seabed, microbial activity, and different physical environment at the bottom of the sea.
- Despite the large variability in porewater concentrations observed in the top 5 cm, calculated benthic fluxes of most transition metals agree with estimated fluxes based on water column concentrations. This likely reflects that the re-oxidation of reduced manganese and iron in the continental shelf top sediment and bottom water scavenges other trace metals and limits their transport.
Reference:
Steiner, Z., Antler, G., Berelson, W. M., Crockford, P. W., Dunlea, A. G., Hou, Y., Adkins, J. F., Turchyn, A. V., & Achterberg, E. P. (2023). Trace Element Geochemistry in North Pacific Red Clay Sediment Porewaters and Implications for Water‐Column Studies. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 37. Access the paper: 10.1029/2023gb007844
