After the Mediterranean Sea one, don’t miss the Arctic present-day total mercury mass balance!
The Arctic mercury (Hg) mass balance is paradoxical since both the natural and anthropogenic sources of Hg into the Arctic atmosphere are low compared to Hg atmospheric deposition rates. Actually, 98% of atmospheric Hg over the Arctic is emitted outside the region and is delivered via long-range air and ocean transport. Dastoor and colleagues (2022, reference below) provide an updated mass balance of the Arctic land and ocean Hg cycle (developed as part of the AMAP 2021 Hg Assessment) which reveals a net atmospheric Hg deposition to the ocean and that the estimates of Hg burial in inner-shelf sediments are probably substantially underestimated. Many of the measurements used to refine the Arctic Ocean mass balance come from the three recent GEOTRACES cruises as well as earlier studies. The mass balance also demonstrates that large pools of Hg have accumulated in permafrost soils that are rapidly thawing in the changing climate, leading to variable Hg discharges to the ocean. This study also establishes the total river Hg inputs (mainly sourced from snowpacks and soils north of 60°N), the role of the shelves surrounding the Arctic in releasing-capturing Hg, and finally the Arctic atmospheric Hg input, and the role of sea ice in modulating Hg air-sea exchange. The revised Arctic Ocean Hg budget is significantly lower than previous estimates, and implies higher sensitivity to future changes in emissions and climate. Best estimates of the fluxes and budgets are summarized in the figure, and their uncertainty estimates are available in the paper.
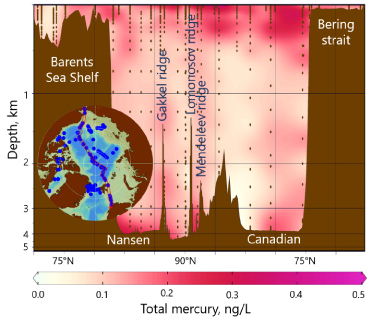
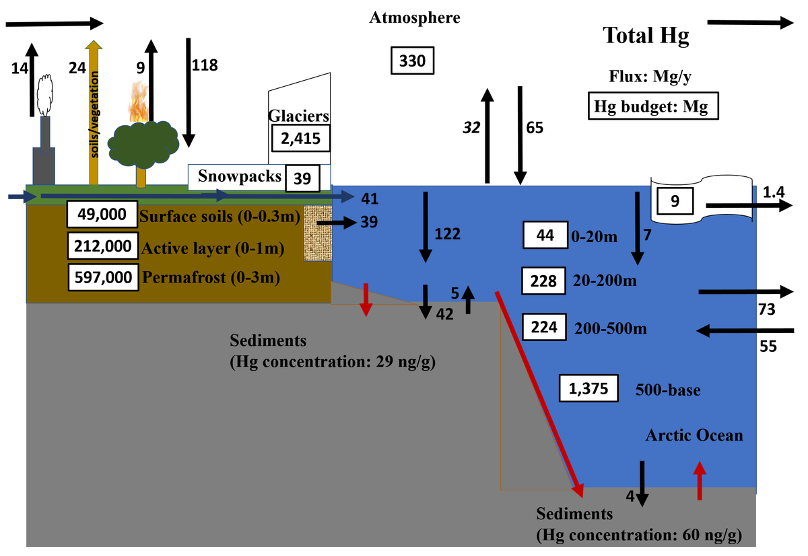
Figure: The mercury concentrations (left) and atmosphere-land-ocean mercury mass fluxes budgets (right) in the Arctic Ocean. The insert map (left) shows the GN01 GEOTRACES cruises transect (red band) and available Hg observations (blue dots). The red arrows indicate missing estimates (right). Shelf region particulate Hg settling (122±55 Mg y-1) from surface waters is the largest Hg removal mechanism in the ocean, and the revised mass balance suggests that Hg burial in shelf sediments (42±31 Mg y-1) is underestimated by up to 52.2±43.5 Mg y-1.
Reference:
Dastoor, A., Angot, H., Bieser, J., Christensen, J.H., Douglas, T.A., Heimbürger-Boavida, L.-E., Jiskra, M., Mason, R.P., McLagan, D.S., Obrist, D., Outridge, P.M., Petrova, M.V., Ryjkov, A., St. Pierre, K.A., Schartup, A.T., Soerensen, A.L., Toyota, K., Travnikov, O., Wilson, S.J., Zdanowicz, C. (2022). Arctic mercury cycling. Nat Rev Earth Environ. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-022-00269-w
