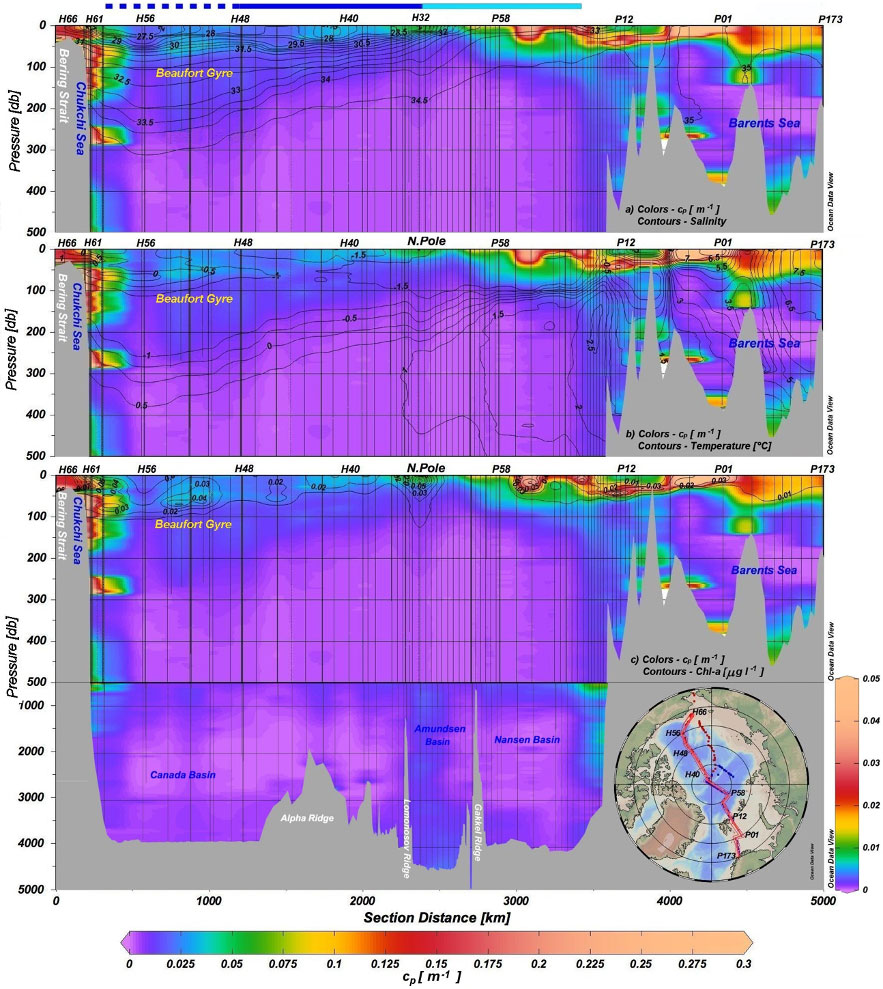
A vivid picture of particle distribution and sources in the Arctic Ocean
Gardner and co-workers (2022, see reference below) proposed an extensive description of particle concentrations and chlorophyll-a fluorescence (Chl-a) distribution along GEOTRACES sections across the Arctic Ocean. The optical data in the sections were paired with particle composition on filtered samples through the whole water column. Particle distributions in the Arctic are affected by currents, stratification, ice coverage and thickness, nutrient and light availability, and biological processes. The combination of cp (a proxy for particular matter and particulate organic carbon) sections plotted with salinity, temperature, and Chl-a contours, adds a background and baseline across the entire Arctic Ocean that is useful in deciphering some of the particle dynamics of the Arctic.
Reference:
Gardner, W. D., Richardson, M. J., Mishonov, A. V., Lam, P. J., & Xiang, Y. (2022). Distribution, Sources, and Dynamics of Particulate Matter Along Trans‐Arctic Sections. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 127(6). Access the paper: 10.1029/2021jc017970
