A thorough estimate of the hydrothermal plumes on neodymium concentration and isotope oceanic cycles
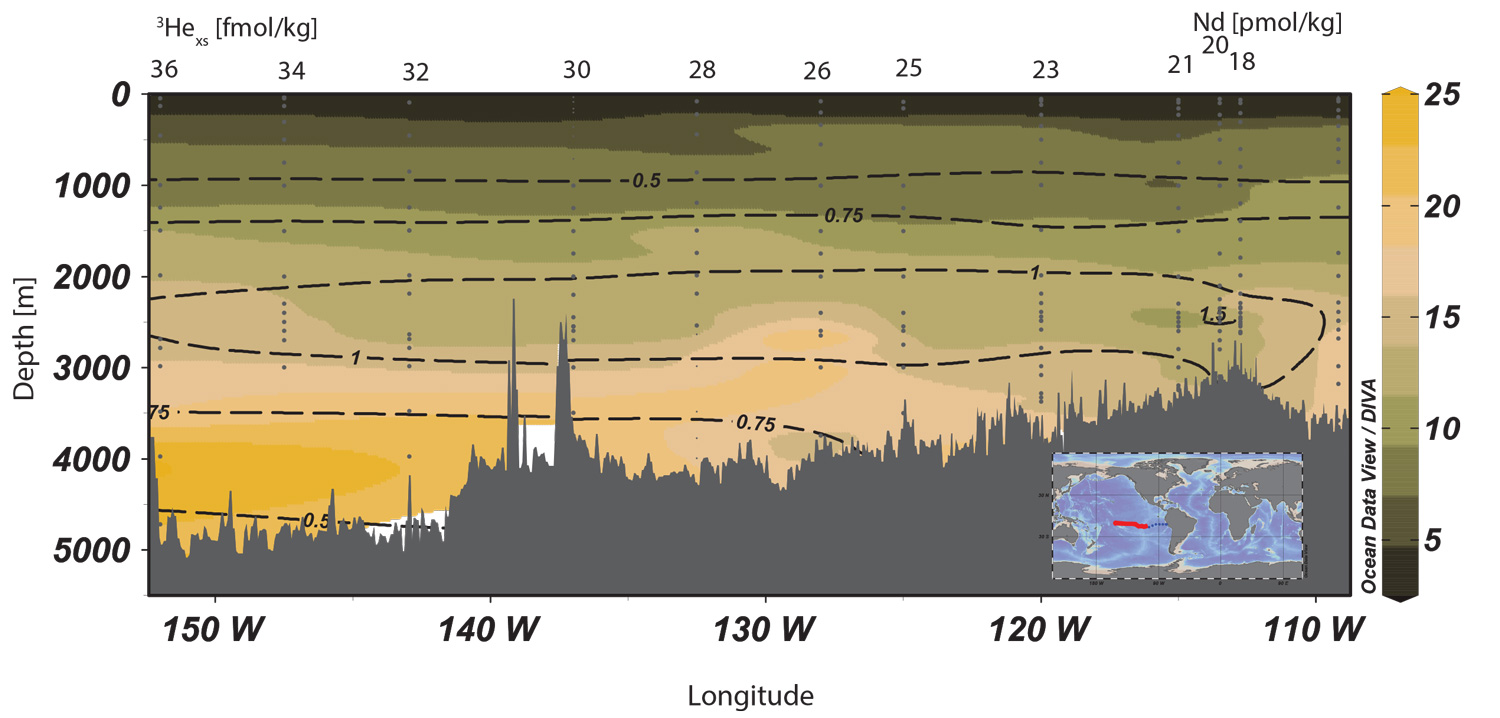
The importance of hydrothermal sources to the global neodymium (Nd) cycle remains under-studied due to limited sampling. To address this issue, Basak and co-workers (2024, see reference below) investigated the influence of particulate matter on Nd distributions in the Southern East Pacific Rise Hydrothermal Plume. To this end, their approach combines tools that are still rarely brought together: dissolved and particulate Nd concentrations, dissolved Nd isotopic composition in the plume, together with suspended matter composition and water mass proportions from an optimum multiparameter analysis. This combination of particle composition, quantification of the Nd non-conservative fraction and partition coefficients established for the first time in a plume revealed that:
- the hydrothermal plume is a sink for dNd, and the intensity of Nd scavenging in the plume generally decreases as distance to the vent increases;
- partition coefficients show that close to the vent, this scavenging, is mainly due to manganese (Mn) oxides close to the vent. They are progressively replaced in importance by iron (Fe) hydroxides as the distance to the vent increase;
- this change may be linked to change in Mn mineralogy in particles;
- below the plume, there is a dNd input, either coming from particle remineralization or from the sediment, what should be investigated further;
- if particles strongly affect dNd distributions, hydrothermal vents have a limited influence on surrounding water mass isotopic composition.
Overall, this study reinforces that Mn oxides and Fe hydroxides are major actor of Nd, and more broadly rare earth elements (REE), scavenging in the ocean. The partition coefficient data contribute to a very scarce dataset, that did not include data in plumes so far, opening new perspectives to improve Nd cycle models.
Reference:
Chandranath Basak, Yingzhe Wu, Brian A. Haley, Jesse Muratli, Leopoldo D. Pena, Louise Bolge, Jessica N. Fitzsimmons, Robert M. Sherrell, Steven L. Goldstein, Suspended particulate matter influence on dissolved Nd concentration and isotopic composition along GEOTRACES section GP16, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, volume 635, 2024, 118692, ISSN 0012-821X. Access the paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2024.118692
