A new model of the oceanic aluminium distribution
Taking into account most of the parameters that govern any trace element’s oceanic behaviour is a challenge, given their number and complexity.
Marco van Hulten and co-workers (2014, see reference below) propose here the most complete model ever written for the oceanic aluminium (Al) distribution. In addition to atmospheric input -which was the only term constraining the Al distribution in a preceding model, see van Hulten et al., 2013-, circulation, sediment re-suspension and biological incorporation by diatoms are considered in this new scheme.
These new sources and sinks are significantly improving the simulated distribution, more specifically a sediment source of Al in the bottom waters of the Northern Atlantic and the velocity fields.
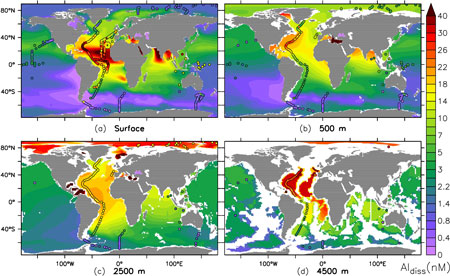
Figure: The dissolved aluminium concentration (nM) of a global model simulation of aluminium. The circles are the observations. The sources in the model comprise the release of Al from dust and from resuspended deep-ocean sediments, the latter depending on the bottom Si concentration. Al is removed by reversible scavenging by biogenic silica. (This figure may be reused, changed and redistributed according to Creative Commons BY-SA. Click here to view the figure larger.)
References:
Van Hulten, M. M. P., Sterl, A., Tagliabue, A., Dutay, J.-C., Gehlen, M., de Baar, H. J. W., & Middag, R. (2013). Aluminium in an ocean general circulation model compared with the West Atlantic GEOTRACES cruises. Journal of Marine Systems, 126, 3–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.05.005 Click here to access the paper.
Van Hulten, M. M. P., Sterl, A., Middag, R., de Baar, H. J. W., Gehlen, M., Dutay, J.-C., & Tagliabue, A. (2014). On the effects of circulation, sediment resuspension and biological incorporation by diatoms in an ocean model of aluminium. Biogeosciences, 11(14), 3757–3779. doi:10.5194/bg-11-3757-2014 Click here to acces the paper.
