What do the first 236-Uranium data reveal in the Arctic Ocean?
Casacuberta and co-authors (2016, see reference below) propose the first set of data for the artificial radionuclide 236-Uranium (236U) in the Arctic Ocean. The novelty of this study compared to the first comprehensive dataset they published in the western North Atlantic Ocean (GEOTRACES GA02 section), is the combination of 236U with 129-Iodine (129I). The 236U/238U and 129I/236U atomic ratios allow them to distinguish the sources of these two artificial radionuclides to the Arctic Ocean, an approach that would not be possible if only using individual concentrations of 236U, 129I or any other anthropogenic radionuclide. For example, using these ratios in a binary mixing model, they could identify Siberian rivers as potential source of artificial radionuclides in the Arctic Ocean, other than the global fallout and the European Reprocessing plants of Sellafield and La Hague. The highly sensitivity of the measurements of these two radionuclides using Accelerator Mass Spectrometry, also allows the detection of very low concentrations of both radionuclides. This dual tracer approach could therefore become an extremely sensitive tool to study isolation ages of deep and bottom waters of the Amerasian Basin.
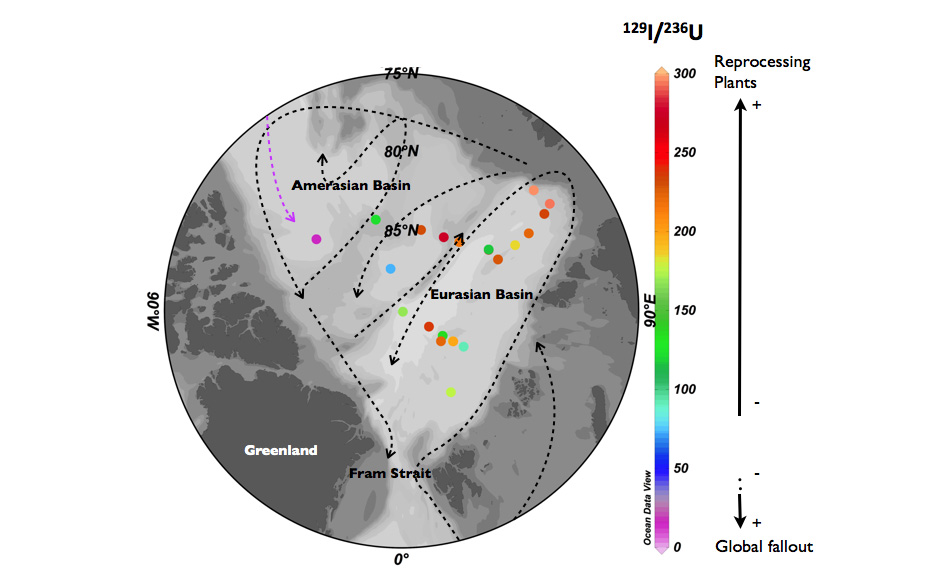
Figure: 129I/236U atom ratio in surface waters of the Arctic Ocean (2011/2012). Atlantic Waters (dashed black line) have higher ratios showing a greater influence of Reprocessing Plants signal. Pacific Waters (dashed purple line) are more influenced by global fallout.
Reference:
Casacuberta, N., Masqué, P., Henderson, G., Rutgers van-der-Loeff, M., Bauch, D., Vockenhuber C., Daraoui A., Walther C., Synal H.-A., Christl M. (2016). First 236U data from the Arctic Ocean and use of 236U/238U and 129I/236U as a new dual tracer. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 440, 127–134. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2016.02.020
