The sedimentary flux of dissolved rare earth elements to the ocean
This work highlights the importance of the sedimentary source of dissolved Rare Earth Elements (REE) to the oceanic waters. Indeed, strong subsurface REE concentration maxima are evidenced in pore fluids in core tops collected along the Californian and Oregon margins (above, within and below the oxygen minimum zone of the North-East Pacific). Diffusive flux of neodymium (Nd) out of the sediments matches preceding estimates of the “missing term” of Nd in modeled global Nd budgets. Also interesting, the decoupling between REE and iron fates in these pore fluids…
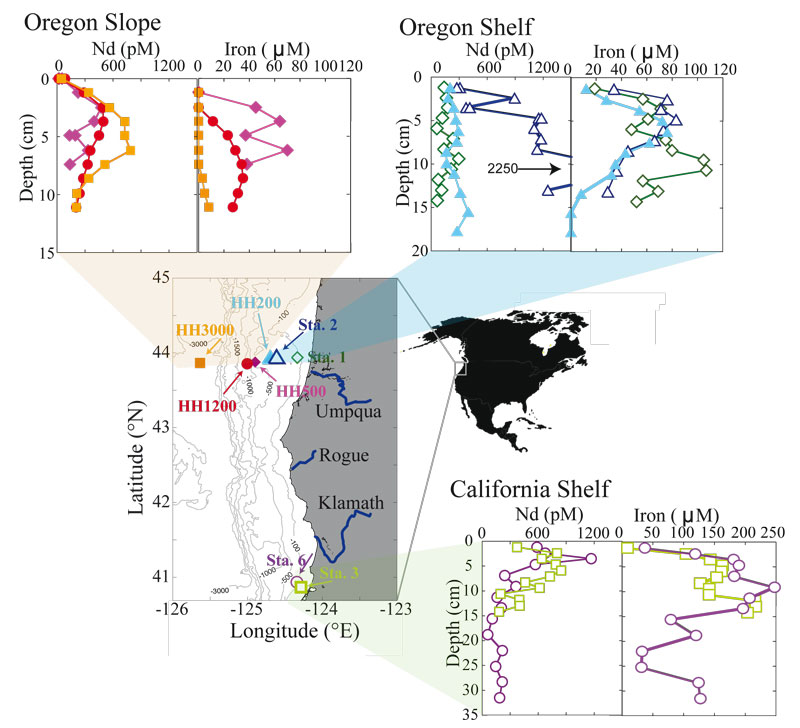
Figure: Site locations and the associated pore fluid profiles. Neodymium (Nd) and iron (Fe) profiles plotted against sediment depth in pore fluids from (clockwise from top left) the Oregon shelf, the Oregon slope, and the California shelf. Filled symbols represent sites unique to this study and open symbols are sites from prior expeditions. Rivers are indicated in blue and labeled. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Abbott, A. N., Haley, B. A., McManus, J., & Reimers, C. E. (2015). The sedimentary flux of dissolved rare earth elements to the ocean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 154, 186–200. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2015.01.010. Please click here to access the paper.
