Submarine Groundwater Discharge as a major source of nutrients in the Mediterranean Sea
The authors are proposing a radium-228 (228Ra) isotope mass balance for the upper Mediterranean Sea to estimate the magnitude of Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) to this basin. Radium isotopes have been widely used as tracers of SGD, mainly because they are enriched in coastal groundwater relative to seawater and behave conservatively once released to the ocean. Naturally decaying with time, they are also good chronometers of processes at play at the continent-ocean interface. 228Ra was also recently used to establish the amount of SGD to the Atlantic and world oceans (Kwon et al., 2014; see here the highlight about this paper). Here, the authors conclude that SGD is a volumetrically important process in the Mediterranean Sea and of larger magnitude than riverine discharge. Importantly, they also demonstrate that SGD is a major source of dissolved inorganic nutrients to the Mediterranean basin, with fluxes comparable to riverine and atmospheric inputs.
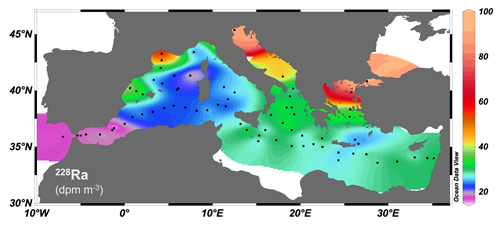
Figure: Interpolated concentrations of 228Ra in surface waters of the Mediterranean Sea (high concentrations are indicated in warm colours red, orange, etc.). Click here to view the figure larger.
References:
Kwon, E. Y., Kim, G., Primeau, F., Moore, W. S., Cho, H.-M., DeVries, T., Sarmiento, J., Charette, M., Cho, Y.-K. (2014). Global estimate of submarine groundwater discharge based on an observationally constrained radium isotope model. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(23), 8438–8444. doi:10.1002/2014GL061574. Click here to access the paper.
Rodellas, V., Garcia-Orellana, J., Masqué, P., Feldman, M., & Weinstein, Y. (2015). Submarine groundwater discharge as a major source of nutrients to the Mediterranean Sea. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(13), 3926–3930. doi:10.1073/pnas.1419049112. Click here to access the paper.
