The biogeochemical ventures of dissolved iron and manganese across the Arctic Ocean
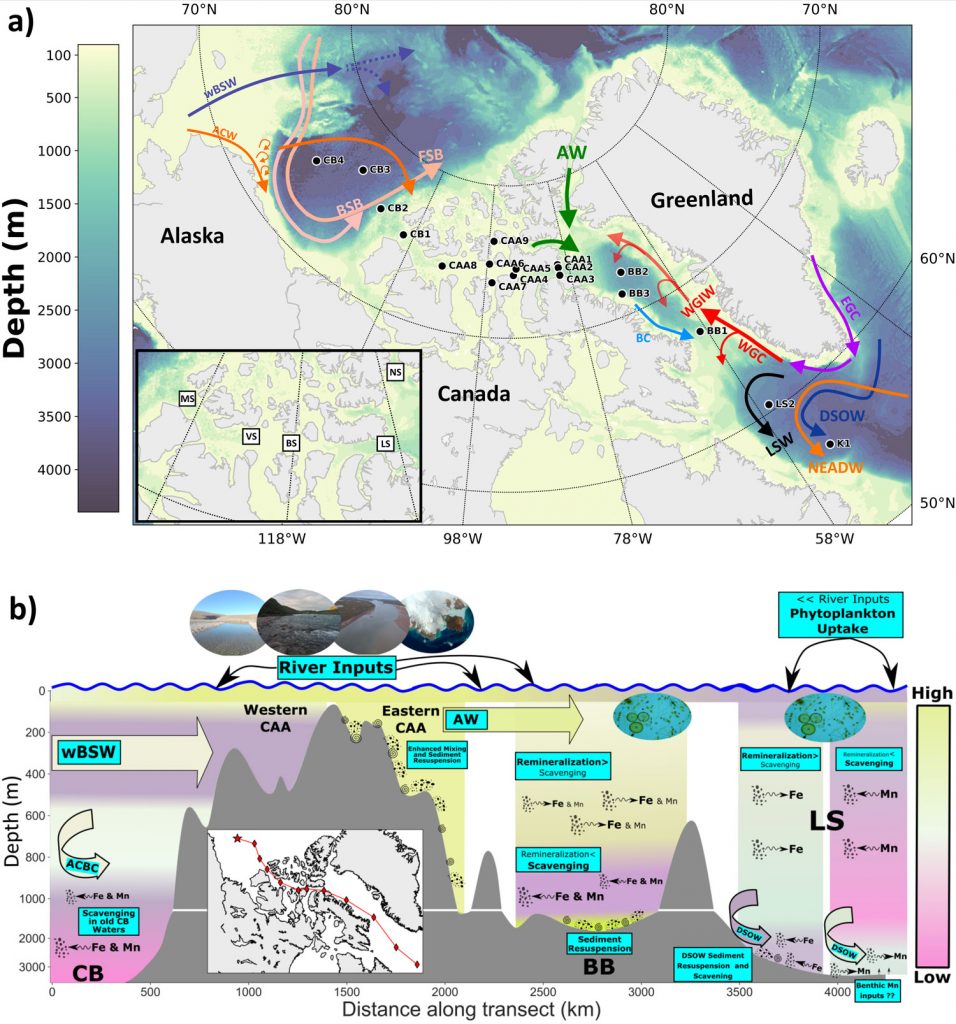
The spatial distributions and biogeochemical cycling of dissolved Fe (dFe) and dissolved manganese (dMn) across the Arctic Ocean were established during summer and fall 2015. The Canadian GEOTRACES transect extended from the Canada Basin (CB) to the Labrador Sea (LS) via the Canadian Arctic Archipelago (CAA).
The surface, subsurface and deep water distributions for both metals are controlled by i) a large variety of processes and ii) a complex balance between sources and sink (river inputs in surface, advective transports and particle remineralization at depth). For example, the highest concentrations are measured in surface waters of the CAA and the CB because these regions are strongly influenced by river inputs. Contrastingly, in the highly productive Baffin Bay and Labrador Sea, the surface waters are markedly depleted in dFe and dMn while organic matter remineralization likely acts as a notable source of these elements to deep waters.
The figure below summarizes the complexity of the processes governing the fate of these elements in the Canadian Arctic Ocean.
Reference:
Colombo, M., Jackson, S. L., Cullen, J. T., & Orians, K. J. (2020). Dissolved iron and manganese in the Canadian Arctic Ocean: On the biogeochemical processes controlling their distributions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 277, 150–174. DOI : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2020.03.012
