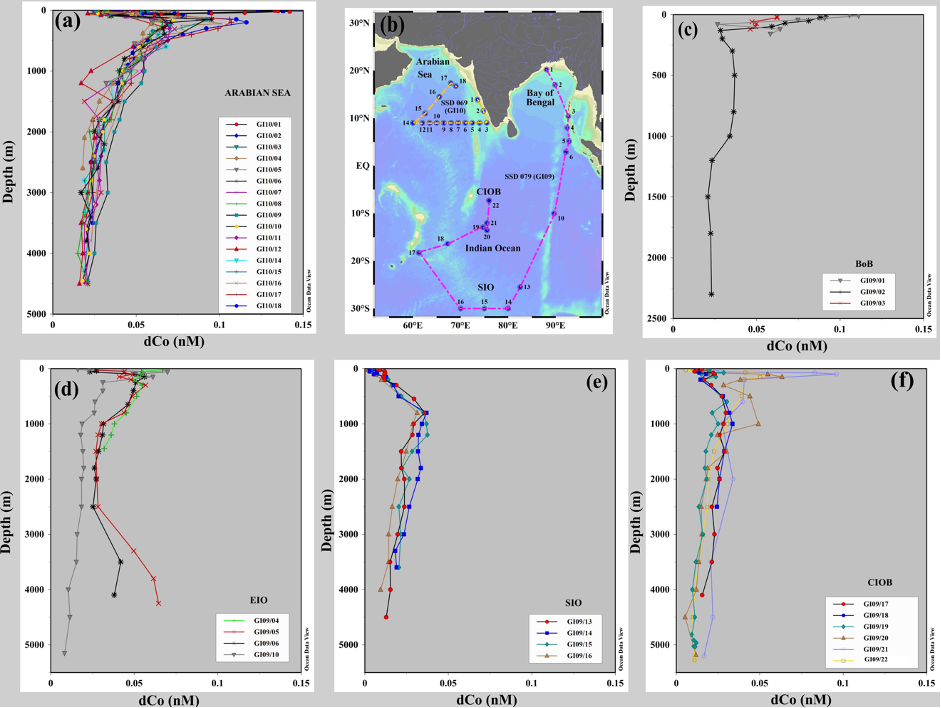
North – South contrasting behavior of dissolved cobalt in the Indian Ocean
Cobalt (Co) plays an important role as a rare bioactive trace metal vital to phytoplankton in the global ocean. Malla and Singh (2024, see reference below) have studied the complex biogeochemical processes of total dissolved cobalt (dCo) in the Indian Ocean and highlight the crucial sources of dCo as fluvial inputs, atmospheric dust, the continental shelf and submarine groundwater discharges to surface waters, while the Java-Sumatra subduction zone acts as a supplier of dCo to deep waters. Although the waters of the Arabian Sea oxygen minimum zone (OMZ) have a dCo cycle similar to that of the World Ocean OMZ, the BoB has a peculiar dCo distribution with surface maxima that are attributed to its large input of fluvial, atmospheric and shelf sediments into surface waters. Authors alert that due to the complex internal cycling of dCo with dissolved oxygen, the global climate change and ocean deoxygenation will severely affect the dCo reservoir in the water column.
Reference:
Malla, N., & Singh, S. K. (2024). Spatial Variability of Dissolved Cobalt in the Indian Ocean Waters: Contrasting Behavior in the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal and the Southern Sector of the Indian Ocean. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 38. Access the paper: 10.1029/2024gb008291
