Labile particulate iron isotopic signatures trace hydrothermal and margin inputs down to the benthic layers in the Eastern Pacific Ocean
For the first time, labile and total particulate iron (pFe) isotopic signatures were measured along a full depth oceanographic section (more than 200 0.8-51 µm-sized particles) in the Eastern Pacific Ocean (GP16 East Pacific Zonal Transect cruise). Marsay and co-authors revealed that:
- a hydrothermal plume emanating from the South East Pacific Rise was identified as a source of labile pFe to the deep ocean, its isotopic composition tracing a quantitative precipitation of iron while the plume mixes with the surrounding seawater,
- export of labile pFe from the Peruvian shelf is isotopically lighter than the hydrothermal one, the negative signature being likely linked to redox cycling within shelf sediments and the Oxygen Minimum Zone,
- far from these two areas, upper ocean [Felabile] was very low, with variable δ56Felabile. Interestingly, the labile pFe isotopic signature are also observed in the sediments of the Benthic Boundary Layer, suggesting that they could help tracing hydrothermal and reduced oxygen conditions in the past ocean.
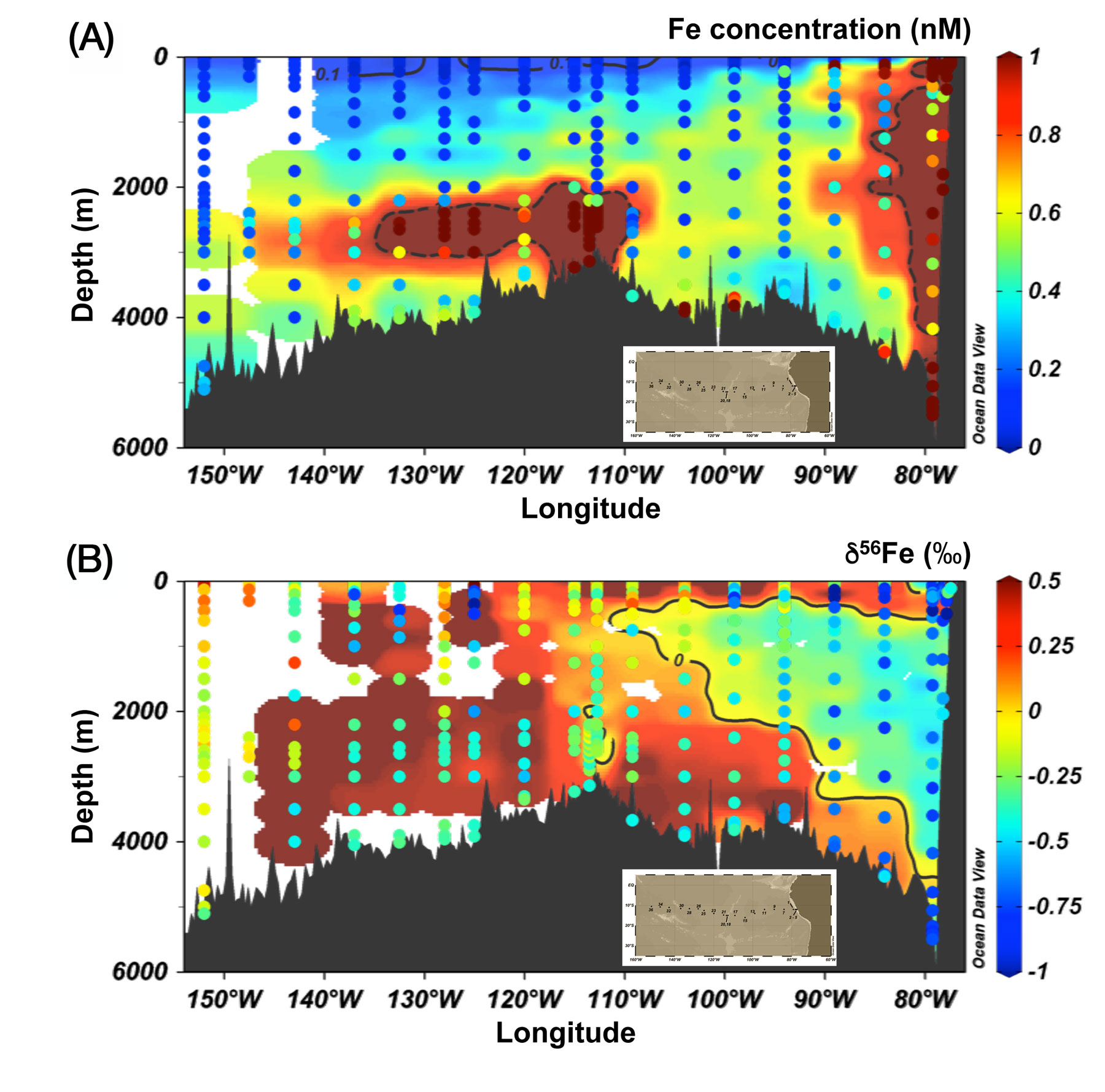
Figure: Iron concentrations and stable isotope data from the GP16 section. a) elevated concentrations of labile particulate Fe (pFelabile; dots) broadly mirror those of dissolved Fe (dFe; shading), with hydrothermal and Peruvian margin sources; contours indicate dFe of >1nM and <0.1nM. b) iron stable isotope data for pFelabile (dots) is typically lighter than for dFe (shading), with both notably lighter near the Peruvian margin; contour indicates d56Fe of 0‰ for dFe. A map indicating where in situ pumps were used to collect particulate material is embedded in figures a) and b). Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference :
Marsay, C. M., Lam, P. J., Heller, M. I., Lee, J.-M., & John, S. G. (2018). Distribution and isotopic signature of ligand-leachable particulate iron along the GEOTRACES GP16 East Pacific Zonal Transect. Marine Chemistry, 201, 198–211. http://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARCHEM.2017.07.003
